Useful compilation of Civil Services oriented - Daily Current Affairs - Civil Services - 05-06-2021
- Polity and Constitution - Supreme strike on sedition case - The Supreme Court of India in June 2021 quashed the sedition case registered against journalist Vinod Dua in Shimla, Himachal Pradesh. This happened a year after the FIR was lodged by a local BJP leader, over Dua’s YouTube show. Dua had criticised the PM Narendra Modi over his handling of the migrant workers' crisis in 2020 pandemic. A bench of justices of the top court ruled that ‘Every journalist is entitled to protection under the Kedar Nath Singh judgment', the landmark verdict of 1962 on the scope of offense of sedition in the IPC. The Kedar Nath judgment had clearly specified the limits of the so-called sedition law (IPC Section 124A). The Section states: "Whoever by words or signs or otherwise brings into hatred or contempt or excites disaffection towards the Government established by law shall be punished, etc." The punishments can be stringent, and extend upto life-imprisonment too. The SC has clarified that unless clear attempts at indulging in violence, or inciting people to violence was established, the law could not be invoked.
- Agriculture - Launch of seed minikits programme - A "Seed Minikit Programme" was launched by the Ministry of Agriculture. Seed Minikits consisting of higher yielding varieties of seeds of Pulses and oilseeds were distributed to farmers. It is wholly funded by the Government of India through the National Food Security Mission. It is a major tool for introducing new varieties of seeds in the farmers’ fields. It will ensure better harvest and better income. It is instrumental for increasing the seed replacement rate. A total of 20,27,318 seed minikits of pulses, more than 8 lakh soybean seed minikits and 74,000 groundnut minikits are to be provided free of cost directly to the farmers under the National Food Security Mission. Oilseeds production in India went from 27.51 million tonnes in 2014-15 to 36.57 million tonnes in 2020-21. Pulses output has increased from 17.15 million tonnes in 2014-15 to 25.56 million tonnes in 2020-21. But despite this, overall production needs to rise, and hence, the programme for introducing new varieties of seeds in fields for increasing the seed replacement rate. [Seed Replacement Rate is the percentage of area sown out of the total area of crop planted in the season by using certified/quality seeds other than the farm saved seed. It is a measure of cropped area covered with quality seed.]
- Governance and Institutions - SAGE initiative - To focus on the needs of India’s fast-rising elderly population, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJ&E) will launch the Senior care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE) project. It will select, support and create a “one-stop access” of elderly care products and services by credible start-ups. Start-ups can apply for being a part of SAGE through the SAGE portal, and will be selected on the basis of innovative products and services across sectors such as health, housing, apart from technological access linked to finances, food management, and legal guidance. The MoSJ&E will act as a facilitator, enabling the elderly to access the products through these identified start-ups. India’s elderly population is on the rise, and the share of elders, as a percentage of the total population in India, is expected to increase from 7.5% in 2001 to almost 12.5% by 2026, and surpass 19.5% by 2050. There is an urgent need to create a more robust elder care ecosystem in India, especially in the post-COVID phase. The SAGE project is shaped on the recommendations of the empowered expert committee (EEC) report on start-ups for elderly.
- Constitution and Law - The EAGLE Act, USA - The Equal Access to Green cards for Legal Employment (EAGLE) Act of 2021 was introduced in the US House of Representatives, aimed at removing the per-country cap on permanent residency visas, or green cards. It seeks to phase out the 7% per-country limit on employment-based immigrant visas and raises the per-country limit on family-sponsored visas from 7% to 15%. It provides for a nine-year period for the elimination of this limit. The 7% limit was introduced in the mid-20th century, which has led countries with relatively small populations to be allocated the same number of visas as a relatively large-population country. However, since the highest number of applicants is from India and China, the EAGLE Act also seeks to reserve visas for ‘Lower Admission States’ for nine fiscal years (FY). While 30% of employment-based visas will be reserved in FY1, this would be reduced to five% in FY 7, 8 and 9. The bill also ensures that “no country may receive more than 25% of reserved visas and no country may receive more than 85% of unreserved visas,” in the nine fiscal years. The EAGLE Act may speed up the petitions for those applying for employment-based green cards. The Act will benefit the US economy by allowing American employers to focus on hiring immigrants based on their merit, not their birthplace. This act will be good for Indian job-seekers who currently rely on temporary visas or await green cards to work in the US.
- Science and Technology - Internet arriving from the Sky - OneWeb has successfully launched 36 satellites in its Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellation, making it reach 218 in-orbit satellites. OneWeb is a global communications company that aims to deliver broadband satellite Internet around the world through its fleet of LEO satellites. The LEO satellites are orbiting the planet since the 1990s, providing people with various communication services. They are positioned around 500km - 2000km from earth, compared to stationary orbit satellites which are approximately 36,000km away. Latency i.e. time needed for data to be sent and received depends on proximity. As LEO satellites orbit closer to the earth, they provide stronger signals and faster speeds than traditional fixed-satellite systems. Since telecom signals travel faster through space than through fibre-optic cables, they also have the potential to rival if not exceed existing ground-based networks. But LEO satellites travel at a speed of 27,000 kph and complete a full circuit of the planet in 90-120 minutes, so individual satellites can only make direct contact with a land transmitter for a short period of time. Hence, massive LEO satellite fleets only can do the job, and that means large capital investment. The problem with such large fleets is that satellites can be seen in the night skies making it difficult for astronomers as satellites reflect sunlight to earth, leaving streaks across images. Satellites travelling at a lower orbit can also interrupt the frequency of those orbiting above them. Earth's near space already has more than 1 million objects larger than 1cm in diameter in orbit, a byproduct of years of space activities. This ‘space junk’ can damage spacecrafts or collide with other satellites.
- Education - TET rules changed - Union Education Ministry decided to extend the validity period of Teachers Eligibility Test (TET) qualifying certificate from 7 years to lifetime with retrospective effect from 2011. The respective State Govts. /UTs will take necessary action to revalidate/issue fresh TET certificates to those candidates whose period of 7 years has already elapsed. This will be a positive step in increasing the employment opportunities for candidates aspiring to make a career in the teaching field. Teachers Eligibility Test is one of the essential qualifications for a person to be eligible for appointment as a teacher in schools for class I to VIII. The TET is conducted by both the central and state governments of India. Most states conduct their own TET. The Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET) is conduted by the Central Board of Secondary Education, Delhi, and the test helps meet the objectives of the provisions of sub-section (1) of Section 23 of The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009. The TET certificate is now valid for lifetime. Earlier, the validity of the TET Certificate was 7 years from the date of passing TET.
- Science and Technology - Clean energy ministerial IDDI - India along with the Govt. of UK launched new workstream to promote industrial energy efficiency under the Clean Energy Ministerial’s (CEM) Industrial Deep Decarbonization Initiative (IDDI), at the 12th Chief Energy Ministerial (CEM). The 12th CEM is ongoing from May 31st and will continue till 6th June 2021. The CEM IDDI is a global coalition of public and private organisations working to stimulate demand for low carbon industrial materials. Coordinated by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), the IDDI is co-led by the UK and India. Additional members include Germany and Canada. The initiative includes organizations like the Mission Possible Platform, the Leadership Group for the Industry Transition, the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and the World Bank. The objective is to tackle carbon intensive construction materials such as steel and cement by infusing green technologies and stimulate demand for low-carbon industrial material.
- Defence and Military - Operation Sagar Aaraksha II - The Indian Coast Guard (ICG), in coordination with Sri Lankan authorities, has been engaged in fighting a major fire onboard the Chemical laden container vessel MV X-Press Pearl anchored off Colombo since 25 May 2021. The coordinated joint operation between India and Sri Lanka undertaken to respond to potential environmental danger has been christened as Sagar Aaraksha-II. Indian Coast Guard ships, including the specialised pollution response vessel Samudra Prahari and offshore patrol vessel Vajra are standby in vicinity to respond to the developing situation. The ICG being an active member of South Asia Co-operative Environment Programme (SACEP) remains committed to its responsibility of safeguarding of the ocean environment in the region.
- Indian Economy - PLI scheme for Telecom and Networking equipment - On 3rd June 2021, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) issued Operational Guidelines for PLI Scheme for telecom & Networking equipment. The DoT had notified the scheme in February 2021. The goal is to make India a global manufacturing hub for telecom and networking products by boosting domestic manufacturing, investments and exports in the sector. The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) is the Project Management Agency (PMA) for the PLI scheme. The scheme will be effective from 1st April, 2021, for a period of five (5) years, i.e. from FY 2021-22 to FY 2025-26. The PLI Scheme will be implemented within the overall financial limits of Rs.12,195 crores only over a period of 5 years. For MSME category, financial allocation will be Rs.1000 crores. The Scheme is open to both MSME and Non-MSME Companies including local and global firms. The Scheme stipulates a minimum investment threshold of Rs.10 crores for MSME and Rs.100 crores for non MSME applicants. Land and building cost will not be counted as investment. Govt. thinks that full utilisation of funds may create an incremental production of around Rs.2.4 Lakh crores with exports of around Rs.2 lakh crores over 5 years. Sadly, there are no employment targets hard-wired into any of the PLI schemes, so young people of India need to wait for other schemes that have a jobs generation target in the crores.
- Indian Politics - Covid updates - (a) India reported 120,529 new Covid-19 cases on Saturday (05th June), the lowest daily spike since April 7. The deaths sadly once again crossed the 3,000 mark, with 3,380 deaths being reported in last 24 hours. (b) An especially infective Covid variant (N440K) has a mutation in its spike protein and had lingered in the southern states along with the now dominant double mutant B.1.617. It is B.1.617 that has wreaked havoc across India during the second wave. The N440K variant is now in Gujarat too. (c) The RBI has cut GDP growth forecast for FY22 to 9.5% from 10.5% due to impact of second wave, which has hit the 1 of FY21-22. NITI Aayog said that economy will recover below than expected now, and grow at a pace of 10%-10.5% in FY22. (d) Biological E’s recombinant protein Covid-19 vaccine, Corbevax, could well emerge as the most affordable of vaccines in the Indian market once it gets emergency use approval (EUA). Corbevax may come at a sub-Rs 500 pricing, for both the doses. (e) NUMBERS - INDIA - Total cases: 28,694,879; New cases: 120,529; Total deaths: 344,101; New deaths: 3380; Total recovered: 26,795,549; Active cases: 1,555,229.
- [message]
- SECTION 2 - DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- [message]
- 1. ECONOMY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
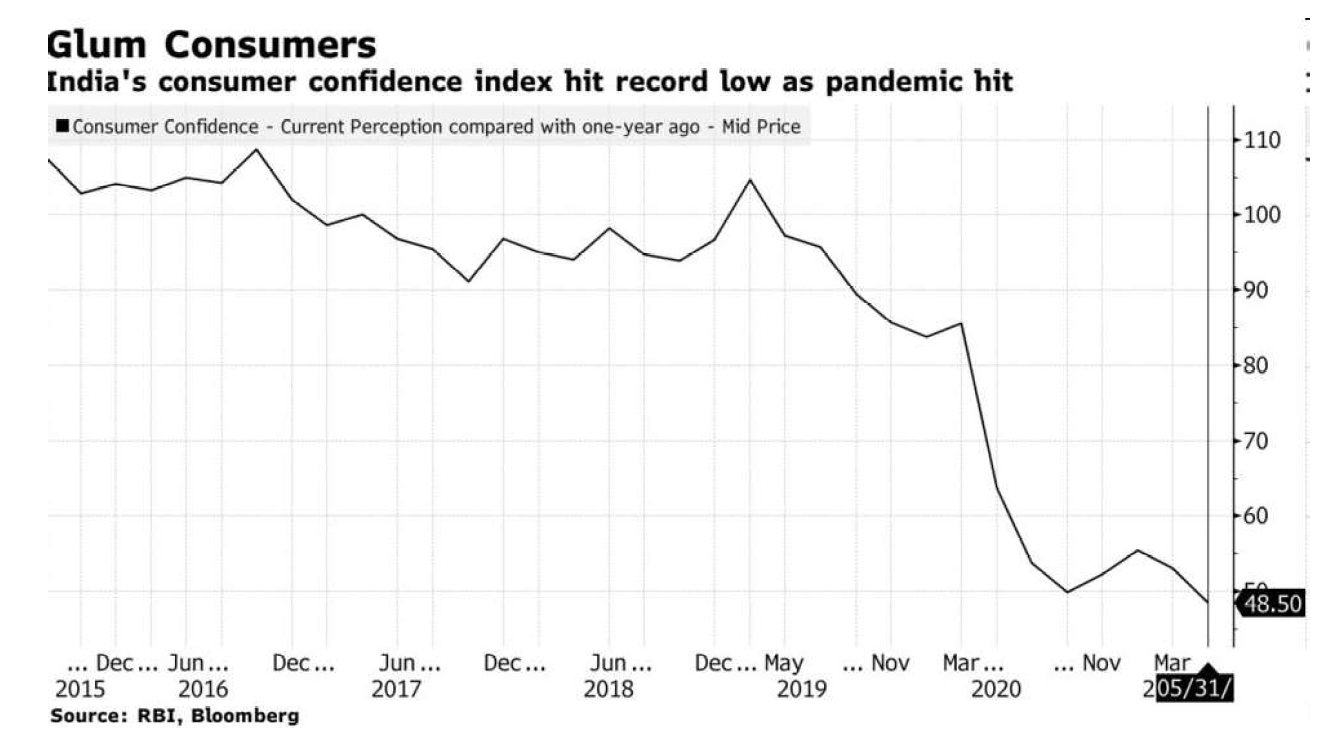
RBI on India's consumer confidence
- The story: Indian consumers’ confidence is dropping fast, largely pushed down by the world’s worst coronavirus outbreak. This was seen in latest Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) consumer confidence survey, where 100 is level that divides pessimism from optimism.
- Data: Respondents were bleak about the year-ahead prospects, with the future expectations index dropping to 96.4 from 108.8 in the period under review. The current situation index fell to a record 48.5 in May from 53.1 in March.
- Household spending weakened in the latest survey round, RBI informed. It cited consumers’ concern about about the economic situation and job prospects. Even essential spending was showing signs of moderation while non-essential spending continues to contract.
- That is not good news for the Indian economy primarily driven by consumption, with high-frequency indicators progressively showing weakness in everything from retail activity to road congestion and power demand to rising unemployment levels.
- One more survey: Another survey pointed to inflation expectations getting well entrenched, adding to the challenge for monetary policy makers who halted interest rate cuts more than a year ago because of gains in price-growth. Sticky underlying price pressures since then have kept the rate-setters from resuming the easing, including at the June 2021 MPC meeting.
- Households’ median inflation perception for the current period jumped by 150 basis points to 10.2% while the inflation expectation for three months rose by 70 basis points to 10.8%, compared to the March 2021 survey.
- Median inflation expectations for one-year ahead also remained at an elevated level at 10.9%.
- Summary: These surveys help RBI gauge the mood in Indian consumer minds, and helps set the direction of monetary policy. Clearly, if the RBI works to push growth, it risks doing little to contain potential inflation.
- The story: RBI continued its Covid relief measures, and has now nudged banks to lend to contact-intensive sectors such as hotels, restaurants, tourism, bus operators and other services by opening a Rs.15,000 crore liquidity window for the lenders (banks). It provided another Rs.16,000 crore to SIDBI to meet the short- and medium-term credit requirements of micro, small and medium enterprises.
- Two moves: These twin moves came along with an expansion of the loan restructuring window for loans taken by individuals and MSMEs, with the eligibility limit for debt doubled to Rs.50 crore. The June measures announced by RBI governor Shaktikanta Das came within a month of a separate facility being made available for the healthcare sector, with banks going ahead and offering loans to individuals.
- Liquidity surplus: With many banks flush with liquidity, large lenders may not need the refinance provided by the central bank for contact-intensive services. But for lenders it is a signal from the RBI that they should extend their loans here.
- The announcement of on-tap liquidity facility of Rs.15,000 crore will ensure credit flow to the contact-intensive sectors and MSMEs including hotels, tourism, aviation, etc, which have been adversely impacted. The RBI is clearly telling them to create credit.
- In May, the RBI had said that banks could restructure loans up to Rs.25 crore advanced to individuals and small business. The restructuring would give the borrowers more time to repay without classifying them as defaulters thus ensuring continued support from the banking system. This limit has now been increased to Rs.50 crore.
- ECLGS: SBI has said that since small businesses were able to avail of liquidity under the emergency line credit guarantee scheme last year, not many sought restructuring. Bankers now feel that the second wave was ebbing, which would reduce the pandemic’s economic impact.
- Summary: RBI's consistent stand on providing liquidity should ultimately result in credit creation at banks' end, else it is of little use.
- [message]
- 2. ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper
More ethanol blending now - Target pulled ahead to 2033
- The story: The Union government announced the advancement of deadline for achieving the 20 per cent target for ethanol blending with fuel, by two years to 2023. The goal is (i) to help save more foreign exchange on the oil import front, (ii) push for a greener future and (iii) help cut sugar industry cut its huge inventory. This is a very ambitious task.
- The directive: The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) directed oil marketing companies (OMCs) to sell ‘Ethanol Blended Petrol” with percentage of ethanol up to 20 per cent, with effect from April 1, 2023. Earlier, it had advanced the deadline from 2030 to 2025.
- This order came within days of the government expanding the scope of the Sugarcane Control Order (SCO), 1966, to treat standalone ethanol making plants as part of the sugar industry.
- With this, ethanol production will no longer be an ancillary activity of sugar production and dedicated ethanol distilleries making ethanol from sugarcane directly can come up.
- They would be able to supply not just ethanol for blending, but also other alcohol products from chemical industrial applications as well as liquor manufacture. Ethanol plants, however, would be bound to pay fair and remunerative prices for the sugarcane they procure from farmers.
- Good for UP: The decision is significant because Uttar Pradesh, the largest sugarcane growing State, recently approved 54 new ethanol plants. In addition, plants that produce ethanol from damaged foodgrains received the nod from the Yogi Adityanath government.
- Ethanol requirement: India will need 850 crore litres of ethanol and around 1,000 crore capacity to reach 20 per cent blending levels. India’s present ethanol production capacity is around 425 crore litres, but only 325 crore litres is available for fuel blending, as a certain quantity is used for making rectified spirt (used in chemical industries) as well as extra neutral alcohol, for making liquor as well as sanitisers.
- With 325 crore litres, oil marketing companies (OMCs) have achieved 8.5 per cent blending this year, up from less than two per cent in 2017. In the next ethanol year (which runs from November to October), the government is aiming to achieve a blending target of 10 per cent.
- Ethanol is currently blended in refineries as well as pump outlets but the OMCs could soon shift it to the refineries.
- Post the new ethanol blending programme announced in 2018, India’s ethanol production capacity has picked up significant pace. However, doubling procurement in one single year would be a difficult task and achieving the 20 per cent target in 2023 is quite ambitious.
- How to achieve it: Experts feel the 20 per cent target is achievable with more sugarcane getting diverted. The sugar industry is carrying over 10 million tonnes of stocks from the last season and for the current season to September 2021 too, a similar amount is expected to be carried over. The Centre has encouraged the diversion by raising the price of ethanol extracted from sugarcane juice to Rs 62.65 a litre.
- The Centre is looking to increase the number of E-20 vehicles that will have 20 per cent ethanol blended in petrol. The Centre might come up with some norms on E20 vehicles from 2023.
- There is no issue with Indian vehicles being able to use fuel blended with 20 per cent ethanol. The Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) has already committed to the government that its members will release new vehicles with E20 material compatible from 2023.
- Risks: In case of a drought in any year, the government may be compelled to give priority to sugar production first. This could impact standalone ethanol plants. Also, the govt. has made it mandatory for OMCs to procure ethanol at higher prices, but this could be unviable in the long run. Since sugar is a politically sensitive commodity, it may get priority over ethanol, particularly in election years.
- Knowledge centre:
- Ethanol blending - Ethanol or C2H5OH is the organic compound Ethyl Alcohol, produced from biomass. It is an ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and has a higher octane number than gasoline, so improves the petrol octane number. An ethanol blend is defined as a blended motor fuel containing ethyl alcohol that is at least 99% pure, derived from agricultural products, and blended exclusively with gasoline. Ethanol has insignificant amount of water in it. Since ethanol is used to oxygenate the gasoline mixture, which in turn allows the fuel to burn more completely and therefore produce cleaner emissions, its use in fuel has obvious benefits for air quality.
- EBP India - The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme was launched in January, 2003. The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- [message]
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Foreign affairs updates
- The Tigray tragedy: More than 5 million people in Ethiopia’s Tigray region — more than 90 percent of its population — were in dire need of emergency food assistance, the United Nations World Food Programme said on Tuesday, as it appealed for a further $203 million in relief funds. The warning comes after U.N. humanitarian coordinator Mark Lowcock alerted the U.N. Security Council of the “serious risk of famine if assistance is not scaled up in the next two months.” Lowcock estimated “over 90 percent of the harvest was lost due to looting, burning, or other destruction, and that 80 percent of the livestock in the region were looted or slaughtered.”
- Iran deal pushed to August 21: Iran said it expected an agreement on a U.S. return to the 2015 nuclear deal (JCPOA) and the lifting of U.S. sanctions to be finalized in August 2021. The official comments effectively quash rumors of an impending deal and stretch the negotiating timeframe until after Iran’s June 18 presidential election. Government has said there were “no obstacles” for negotiators in the Vienna talks but that “some differences such as Trump’s sanctions and Iran’s measures need to be worked out.”
- AU suspends Mali: The African Union has suspended Mali’s membership for the second time in less than a year following last week’s coup in which interim President Bah Ndaw and Prime Minister Moctar Ouane were arrested and pressured to resign by the Mali’s military. The African Union has also threatened Mali with sanctions if it did not embrace “an unimpeded, transparent and swift return to the civilian-led transition.” Assimi Goita, the leader of the August coup which toppled Mali’s previous government, assumed the role of president. The AU’s move follows a similar suspension by the West African bloc ECOWAS on Sunday.
- Canada’s mass graves: After the remains of 215 children were found in May 2021 at a former Indigenous residential school in Canada, Indigenous groups are now calling for a search for more unmarked mass graves at residential school sites throughout Canada. The children, some as young as three, were buried in British Columbia at Kamloops Indian Residential School, one of the state-funded institutions where about 1,50,000 Indigenous children were forcibly sent between 1831 and 1996 to be “assimilated” into white Canadian society in what the country’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission has called a “cultural genocide.” The Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said that the discovery was not an “isolated incident,” and that looking for more mass graves is “an important part of discovering the truth,” but he did not commit to any plans.
- Global oil prices: Oil prices rose to their highest level of the pandemic period as Brent crude futures traded at over $70 a barrel for the first time in two and a half years. The rise reflects expectations of greater fuel demands as the U.S. and Chinese economies show signs of recovery heading into the summer, and builds on the confidence of OPEC+ countries, who agreed to continue easing oil supply restrictions through July 21.
India's abstention from resolution against Israel
- The story: In May, Palestine blamed India for suppressing the human rights of all people as India abstained from the latest resolution on the Palestinian issue.
- Details: India abstained from voting on a resolution at the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) that came up in the backdrop of the latest round of conflict (May 2021) between Israel and Gaza strip, the coastal part of the Palestinian territories. The UNHRC is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations (UN) system responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the world.
- Points to note: The resolution called on the UNHRC to set up a permanent commission to probe human rights violations in Gaza, West Bank and Palestine. It was adopted with the vote of 24 members. Nine voted against, and 14, including India, abstained. Among the countries that abstained on the vote, along with India, were France, Italy, Japan, Nepal, the Netherlands, Poland, and South Korea. China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Russia were among those who voted in favour; Germany, the UK, and Austria voted against the resolution. As it was passed, an independent commission of inquiry was formed to investigate violations of international law by Israel.
- Palestine's stand: The resolution is not an aberration to the Human Rights Council, but the by-product of extensive multilateral consultations. It is the consolidation of years and thorough investigations into and reporting on Israel’s grave violations by States, UN’s experts, Human Rights Treaty bodies, and international organisations. The Palestinian people were deprived of applicability of international human rights law. The root causes of the injustice against the Palestinian people was dispossession, displacement, colonisation by Israel. So India’s abstention stifles the important work of Human Rights Council at advancing human rights for all peoples, including those of the Palestinian people.
- India’s position on Israel-Palestine issue: India recognised Israel in 1950 but it is also the first non-Arab country to recognise Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian. India is also one of the first countries to recognise the statehood of Palestine in 1988. In 2014, India favored UNHRC’s resolution to probe Israel’s human rights violations in Gaza. Despite supporting the probe, India abstained from voting against Israel in UNHRC in 2015. As a part of "Link West Policy", India has de-hyphenated its relationship with Israel and Palestine in 2018 to treat both the countries mutually independent and exclusive. In June 2019, India voted in favor of a decision introduced by Israel in the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) that objected to granting consultative status to a Palestinian non-governmental organization. In March 2021, International Criminal Court (ICC) launched investigatations into the war crimes in Palestinian territories occupied by Israel (West Bank and the Gaza Strip). Israel wanted India to take a stand against it, however it did not happen. India has tried to maintain the image of its historical moral supporter for Palestinian self-determination, and at the same time to engage in the military, economic, and other strategic relations with Israel.
- Summary: India’s policy on the longest running conflict in the world has gone from being unequivocally pro-Palestine for the first four decades, to a tense balancing act with its three-decade-old friendly ties with Israel. In today's multipolar world, India needs to have a balanced approach. All regional powers should envisage peace between the two countries on line of Abraham Accords.
- [message]
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
Hong Kong finally crushes Tiananmen anniversary event
- The story: A Hong Kong park has traditionally hosted huge vigils on the anniversary of China’s deadly Tiananmen Square crackdown of 1989. In 2021, that park lay empty for the first time as police blocked access, but flashes of defiance still flickered across the city.
- The anniversary: Huge crowds have routinely gathered in Hong Kong’s Victoria Park to mark the anniversary of Chinese troops crushing peaceful democracy protests in Beijing’s Tiananmen Square on June 4, 1989. Thousands were killed in the crackdown, and China has since blocked all news pertaining to the event. The crackdown was a landmark event for the Communist Party, where Deng Xiaoping used the State's force to crush all dissent.
- Censored: All public commemorations are forbidden on the mainland PRC and, until recently, semi-autonomous Hong Kong was the one place in China where large scale remembrance was still tolerated. This year’s vigil was banned at a time when authorities are carrying out a sweeping clampdown on dissent following huge and often violent democracy protests two years ago.
- New Hong Kong: Ever since Xi Jinping has tightened control over HK, all such events are out of question. For the first time in 32 years, candle carrying mourners were kept out. Activists who approached the park were stopped and searched, while officers used loud hailers and signs to call for people to disperse from nearby streets.
- Taiwan's stand: Taiwan’s people will never forget the crackdown in Tiananmen Square, President Tsai Ing-wen said. Tsai said, “For all Taiwanese who are proud of their freedom and democracy, they will never forget about this day.” It is also planning to undertake genome sequencing of a sample of nearly 1000 Indian rural youth to determine unique genetic traits, susceptibility (and resilience) to disease.
CSIR - Council of Scientific and Industrial Research
- The story: The CSIR has contributed significantly to India's forward march in science. Recently, the CSIR Floriculture Mission was approved for implementation in 21 States and Union Territories of India. It was established in 1942, at New Delhi.
- Information: It is the largest research and development (R&D) organisation in India, with a pan-India presence and a dynamic network of 37 national laboratories, 39 outreach centres, 3 Innovation Complexes and 5 units. It is ranked 37th among 1587 government institutions worldwide and is the only Indian organization among the top 100 global government institutions, according to the Scimago Institutions Ranking World Report 2021. The CSIR holds the 7th rank in Asia and leads the country at the first position.
- The Prime Minister is the President (Ex-officio) and the Union Minister of Science and Technology is the Vice President (Ex-officio).
- CSIR is funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology and it operates as an autonomous body through the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Objectives: It is mandated to condut scientific and industrial/applied research of national importance. It covers a wide spectrum of streams such as Radio and space physics, oceanography, biotechnology, nanotechnology, information technology, etc. It provides significant technological intervention in many areas with regard to societal efforts which include the environment, health, drinking water, food, housing, energy, farm and non-farm sectors.
- Initiatives:
- During pandemic - The CSIR set up five technology verticals for addressing the emerging situation due to pandemic (i) Digital and Molecular Surveillance, (ii) Rapid and Economical Diagnostics, (iii) Repurposing of Drugs, Vaccine and Convalescent Plasma Therapy, (iv) Hospital Assistive Devices and PPEs (Personal Protective Equipment), (v) Supply Chain and Logistics Support Systems.
- Strategic - It developed indigenous Head-Up- display (HUD) for Indian Light Combat Aircraft, Tejas. HUD aids the pilot in flying the aircraft and in critical flight maneuvers including weapon aiming.
- Energy & Environment - India’s first lithium ion battery fabrication facility based on indigenous novel materials for making 4.0 V/14 h standard cells has been established.
- Agriculture - (i) Samba Mahsuri Rice Variety: It developed a Bacterial Blight Resistant Rice, (ii) Rice Cultivar (Muktashree): A rice variety has been developed which restricts assimilation of Arsenic within permissible limits, (iii) White-fly resistant Cotton variety: Developed a transgenic cotton line which is resistant to whiteflies, etc.
- Healthcare - Genomics and other omics technologies for Enabling Medical Decision – GOMED: It has been developed by the CSIR which provides a platform of disease genomics to solve clinical problems.
- [message]
- 5. POLITY AND CONSTITUTION (Prelims, GS Paper 2, GS Paper 3)
Major changes in environment laws arriving
- The story: India's environment ministry (MoEFCC) is working on a radical change to the country’s environmental law regime, including changes in the important Wildlife Protection Act 1972. The move comes amidst concerns that the changes are being made to make it easier to develop infrastructure and industrial projects, even in environmentally sensitive areas.
- Preliminary work on: The ministry’s wildlife division has prepared a Cabinet note to amend the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which is yet to be cleared by the Cabinet; a similar note on the amendment to Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 has also been finalised after circulating it internally among ministries. The FC Act amendment has been finalised with inputs from ministries. The first draft was cleared and is ready to be sent for Cabinet nod.
- On April 8, the ministry called for expression of interest from consulting and law firms to prepare a new draft amendment to the Indian Forest Act, 1927.
- A private law firm is preparing a draft environmental management act which will subsume the Air Act 1981, Water Act, 1974, and the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, and serve as an overarching law for all infrastructure and industry projects.
- This will also cover regulations of the coastal areas and islands through the Coastal Regulation Zone provisions.
- The idea is to “streamline processes and to remove any ambiguity in provisions. This will make the job easy for everyone.”
- What changes: The amendment in the FC Act, for instance, will mainly focus on finalising the definition of forests. The Supreme Court in 1996 in the "T N Godavarman Thirumalpad Vs Union of India & Ors" case held that the word ‘forest’ must be understood according to its dictionary meaning. It also said that irrespective of whether an area is a forest as per revenue records, it will be covered by the FC Act, and cannot be used for any non-forestry activity without the Centre’s permission if it meets the dictionary meaning. To avoid any further confusion, we will ensure that states which haven’t yet recognised forests as per dictionary meaning do so immediately and those that have can finalise the area accordingly. It will also clarify that plantation on non-forest land will not be recognised as forest in future. They are a totally different category and can be harvested by people who have planted them. This will also facilitate plantations.
- Criticism: Experts say that a cautious, democratic and ambitious environmental agenda is the way forward to uphold social justice and reduce risks to business. Instead, the government has floated at least one legal change every month that is regressive, will increase resource conflicts and will not help defend ecological vulnerabilities. Most of these have been designed in close door expert meetings, or instructed through office orders.
- Relaxing it all: Earlier in 2021, when the second wave of Covid-19 was ravaging the country, the environment ministry issued some contentious circulars. In a letter dated March 22 to additional chief secretary (forest)/ principal secretary (forest) of all state governments and Union territories, the ministry stated that a state government/UT administration will not impose any additional condition on infrastructure projects after in-principle approval has been accorded by the Centre. The move will further centralise powers to monitor infrastructure projects and constrain state government’s decision-making in issues related to forest and wildlife conservation.
- Summary: In May 2021, the ministry made provisions to expedite forest clearances for “critical infrastructure projects” in Left-wing extremism (LWE)-hit districts and those related to defence and security in border areas by delegating them to the regional offices of the ministry and making clearances time bound. Decisions on major projects such as granting terms of reference (TOR) for a township and area development project proposal on the Great Nicobar Island are likely to impact turtle and megapode nesting sites.
- [message]
- 6. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (Prelims, Various GS Papers)
The Artificial Sun rises in China
- The story: Nations are striving to build an "artificial Sun" right here on planet Earth. So, they are trying to run controlled fusion reactions. In May, China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) achieved a peak temperature of 288 million degrees Fahrenheit, which is over ten times hotter than the sun. In 2020, South Korea’s KSTAR (Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research) reactor set a new record by maintaining a plasma temperature of over 100 million degrees Celsius for 20 seconds.
- The Tokamak concept: The 'tokamak' is an experimental machine designed to harness the energy of fusion. Inside it, the energy produced through the fusion of atoms is absorbed as heat in the walls of the vessel. Like a conventional power plant, a fusion power plant uses this heat to produce steam and then electricity by way of turbines and generators.
- Points to note: The EAST reactor is an advanced nuclear fusion experimental research device located at the Institute of Plasma Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ASIPP) in Hefei, China. The EAST first became operational in 2006.
- The purpose of the 'artificial sun' is to replicate the process of nuclear fusion, which is the same reaction that powers the sun.
- This is part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) facility, which will become the world’s largest nuclear fusion reactor when it becomes operational in 2035.
- The ITER Members include China, the European Union, India, Japan, Korea, Russia and the United States.
- Technical working: This concept is based on the nuclear fusion process that running in the core of all stars, including the Sun. For nuclear fusion to occur, tremendous heat and pressure are applied on hydrogen atoms so that they fuse together. The nuclei of deuterium and tritium - both found in hydrogen - are made to fuse together to create a helium nucleus, a neutron along with a whole lot of energy. The gaseous hydrogen fuel is heated to temperatures of over 150 million degrees Celsius so that it forms a hot plasma (electrically charged gas) of subatomic particles. With the help of a strong magnetic field, the plasma is kept away from the walls of the reactor to ensure it does not cool down and lose its potential to generate large amounts of energy. The plasma is confined for long durations for fusion to take place.
- Other Tokamaks in China: Apart from the EAST, China is currently operating the HL-2A reactor as well as J-TEXT. In December 2020, HL-2M Tokamak, China’s largest and most advanced nuclear fusion experimental research device, was successfully powered up for the first time — a key milestone in the growth of China’s nuclear power research capabilities.
- Importance: It is significant as far as China’s green development is concerned. Nuclear fusion is a process through which high levels of energy are produced without generating large quantities of waste. Unlike fission, fusion also does not emit greenhouse gases and is considered a safer process with lower risk of accidents.
- Knowledge centre:
- Nuclear reactions - A nuclear reaction is the process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Sp a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another.
- Fission and fusion - In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom splits into two daughter nuclei. This decay can be natural spontaneous splitting by radioactive decay, or can actually be simulated in a lab by achieving necessary conditions (bombarding with neutrons, alpha particles, etc.). The resulting fragments tend to have a combined mass which is less than the original. The missing mass is usually converted into nuclear energy. Currently all commercial nuclear reactors are based on nuclear fission. In nuclear fusion, two lighter nuclei are combined into a heavier one. Such fusion reactions are the source of energy in the Sun and other stars, but it takes considerable energy to force the nuclei to fuse. The conditions needed are extreme – millions of degrees of temperature and millions of pascals of pressure.
- Hydrogen bomb - The hydrogen bomb is based on a thermonuclear fusion reaction. However, a nuclear bomb based on the fission of uranium or plutonium is placed at the core of the hydrogen bomb to provide initial energy, that can actually lead to a fusion reaction.
- [message]
- 7. SOCIAL ISSUES (Prelims, GS Paper 2)
Pandemic in India - Food habits of the poor changed
- The story: Even before the pandemic hit, India was one of the world’s most malnourished countries. Various indicators showed it from time to time. In such a country with such poor development indicators, Covid-19 hit India’s poor first, and hit then hard. The world’s harshest lockdown with little planning made the situation truly worse.
- Data points: A new research paper by economists Jean Drèze and Anmol Somanchi has analysed survey data to look at the impact of India’s first Covid-19 lockdown in 2020 on food deprivation. Their conclusion is grim: “the lockdown and the economic recession that followed led to a severe nutrition crisis”.
- Income crash: The first impact of the lockdown was obviously on incomes and employment as India put in place the world’s harshest restrictions which shut down almost all economic activity. Across the board, surveys showed a drastic drop in incomes compared to pre-lockdown levels.
- A survey by IDinsight found that the average weekly income of non-agricultural respondents crashed from Rs 6,858 in March 2020 to Rs 1,929 in May, and was still around that level in September. The proportion of non-agricultural respondents who reported zero days of work shot up from 7.3% in early March to 23.6% in the first week of May and was still as high as 16.2% in the first week of September.
- Another survey by consulting firm Dalberg found that primary income earners of 52% of households were unemployed in May despite having a job before the lockdown and another 20% were still employed but earning less than before.
- Drèze and Somanchi argue that this hit was not temporary and it was “doubtful that income and employment ever regained their pre-lockdown levels before a second wave of the Covid-19 epidemic hit the country in early 2021”.
- Food insecurity: Like with incomes, surveys across the board pointed an alarming rise in food insecurity. Depending on the survey, between 53%-77% respondents argued that they were eating less after the pandemic hit than before. Even more alarmingly, lifting the lockdown had a rather small effect. A survey by the Centre for Sustainable Employment at the Azim Premji University, for example, found that even in the September-November period, the proportion of people eating less than what they did before the start of the pandemic was as high as 60%. (It was 77% during the lockdown).
- Poor and informal: ActionAid found that 35% of surveyed informal, mainly migrant workers were eating fewer than two meals a day in May. Similarly, a survey by Pradan, another non-profit, covering informal sector workers in rural areas of 13 states found that half of them were eating fewer meals than before. The quantity of food was not the only red flag – so was it nutrional value. Data from the Centre for Monitoring the Indian Economy (CMIE) shows that while expenditure on cereals remains almost constant, there was a drastic decline in money spent on nutrient and protein-heavy food such as eggs, meat, fish and fruits. And this holds across income groups. On meat and fish, in fact, the expenditure of the top 25% income group drops to levels below that for the middle 50% pre-lockdown.
- The good news: The silver lining in this was the performance of India’s public distribution system, which supplies either free or highly subsidised foodgrains to Indians. During the lockdown, both state governments as well as the Union government announced relief measures such as free and increased rations. Dalberg, for example, notes that as many as 89% of Indians received PDS grain during lockdown. Moreover, a similar number also received free grain as per temporary lockdown schemes.
- Summary: Given that a second Covid-19 wave in India this summer had led to most of the country going under state-implemented lockdowns, the research paper recommends that a “second, stronger wave of relief measures is essential to avoid a repeat of last year’s tragic humanitarian crisis”. Jean Drèze has also recommended cash transfers as a way to help Indians hit hard by the pandemic lockdowns. All operational problems (like rations cards etc.) must be resolved quickly.
- [message]
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
- The story: India’s largest power utility, NTPC Ltd, has become a signatory of UN Global Compact’s CEO Water Mandate. NTPC is a government owned electricity board, formerly knowns as National Thermal Power Corporation Limited. It is engaged in business of generation of electricity and allied activities.
- Points to note: The CEO Water Mandate is a coveted league of companies focusing on efficient water management. NTPC now has joined a select group of business leaders who recognize importance of water stewardship and is working to conserve water.
- NTPC’s water conservation: It has taken several measures across its plant locations for water management. It will now follow the policy of 3 Rs - reduce, reuse, recycle for water conservation and management while generating power.
- CEO Water Mandate: It is a UN Global Compact initiative which demonstrate commitment and efforts of companies to enhance their water and sanitation agendas in line with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It has been designed to assist companies in developing, implementing and disclosing comprehensive water strategies and policies. It provides a platform for companies to link with like-minded businesses, public authorities, UN agencies, civil society organizations etc.
Ladakh launches YounTab scheme
- The story: Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh, RK Mathur, launched the YounTab scheme for students. Under the scheme, about 12,300 tablets were distributed among them in Leh.
- YounTab scheme: It is an initiative of Department of School Education. It was launched with the technical support of Information Technology Department. Under the scheme, 12,300 tablets with preloaded online and offline content like textbooks, video lectures and online class applications would be distributed among students from Class 6th to 12th in government schools. Scheme was launched as an attempt for long term technology infusion in education system.
- Ladakh: This UT is administered by India and is a part of larger Kashmir region, which has witnessed disputes between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. Ladakh was established as separate UT on October 31, 2019 after Jammu & Kashmir Reorganisation Act was passed. It is bordered by Tibet Autonomous Region in east, Himachal Pradesh in south, Jammu & Kashmir in west, and Xinjiang across the Karakoram Pass in north. It extends from Siachen Glacier in Karakoram range to Great Himalayas from north to south. Its eastern part comprising of uninhabited Aksai Chin plains is under Chinese control since 1962. Largest town in Ladakh is Leh followed by Kargil. Leh district comprise of Shyok, Indus and Nubra river valleys. While Kargil district comprises of Dras, Suru and Zanskar river valleys. It is the 2nd least populated UT in India.
Denmark approves Artificial Island off Copenhagen
- The story: The Parliament of Denmark has approved plans for an artificial island which will house 35,000 people and help in protecting port of Copenhagen from rising sea levels.
- Lynette Holm Island: This giant island would have an area of 1 sq mile and would be connected to mainland through ring road, tunnels and metro line. Plans include construction of a dam system across its perimeter. This dam will help in protecting the harbour from rising sea levels and storms.
- Troubles: The construction is facing opposition from environmentalists as it may have an adverse effect on environment. It will lead to transportation of materials by road through large numbers of vehicles. About 350 lorry journeys will be required in a day through Copenhagen once the construction has started. Thus, concerns over moment of sediments at sea and impact on ecosystem and environment are being raised. Following this, a case against the development of Lynette Holm has been filed before European Court of Justice by environmental groups.
- [message]
9.1 Today's best editorials to read
- We offer you 7 excellent editorials from across 10 newspapers we have scanned.
- [message]
- SECTION 3 - MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)