Useful compilation of Civil Services oriented - Daily Current Affairs - Civil Services - 13-03-2021
- Healthcare and Medicine - Maha reports nearly 16k new COVID cases in biggest 1-day spike this year - Maharashtra has recorded 15,817 new COVID-19 cases on 12-03-2021 in the biggest one-day spike in coronavirus cases in the state in 2021. The state also recorded 56 deaths and 11,344 COVID-19 recoveries on Friday. The last biggest single-day COVID-19 spike of the year in Maharashtra was recorded on Thursday when the state reported 14,317 cases. India added 24,882 fresh COVID-19 cases on 12-03-2021 - the highest daily rise in the last 83 days - taking its tally to 1.13 crore cases. The number of fresh infections is nearly seven per cent higher than one day before, when India registered 23,285 cases. Overall, India has now recorded 1,13,33,728 cases since the outbreak a year ago. Maharashtra, Kerala, Punjab, Karnataka, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu account for 85.6 per cent of the new cases. India is witnessing the worrying spike in the rate of Covid-19 infection amid an intensive and accelerating inoculation drive through which more than 2.80 crore (2,80,05,817 ) vaccine doses have been administered to the benficiaries so far.
- Science and Technology - ISRO launches sounding rocket RH-560 - Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched the sounding rocket, RH-560, at Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota Range on 12-03-2021. The RH-560 will study attitudinal variations in the neutral winds and plasma dynamics. Sounding rockets are one or two-stage solid propellant rockets used for probing the upper atmospheric regions and for space research, ISRO stated. They also serve as affordable platforms to test or prove prototypes of new components or subsystems intended for use in launch vehicles or satellites. At present, Isro has three versions of sounding rockets- RH-200, RH-300-Mk-II and RH-560-Mk-II capable of carrying 8-100kg payload and reach an altitude of 80 to 475km. The launch of the first sounding rocket US made ‘Nike Apache’ from Thumba near Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala on November 21, 1963, marked the beginning of the Indian Space Programme. Later days saw launching of two-stage rockets imported from Russia (M-100) and France (Centaure). While M-100 could carry a payload of 70 kg to an altitude of 85 km, the Centaure was capable of reaching 150 km with a payload of approximately 30 kg. In 1965, ISRO started launching a series of own sounding rockets named Rohini from TERLS. RH-75, with a diameter of 75mm was the first truly Indian sounding rocket, which was followed by RH-100 and RH-125 rockets. Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, born on August 12, 1919, in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, played a major role in setting up India's space research infrastructure. He came to be known as the Father of the Indian space programme.
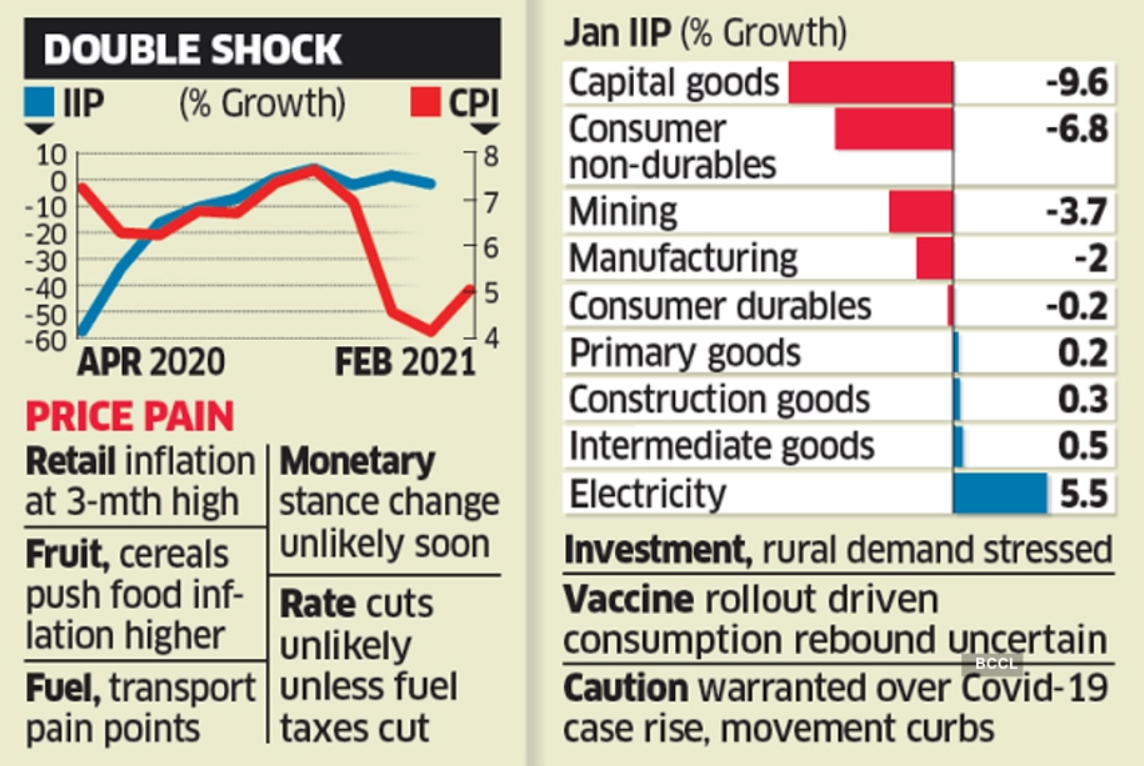
- Governance and Institutions - Retail inflation at 3-month high of 5.03% in February - Retail inflation rose to a three-month high of 5.03% in February, owing to higher food prices, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation stood at 4.06% in January. Inflation in food and beverages rose to 4.25%, compared to a rise of 2.67% in January. The month-on-month rise in the food basket was led by a rise in prices of oils and fats which rose 20.78 per cent in February, while that of pulses and products rose 12.54 per cent, the data showed. Non-alcoholic beverages gained 13.92 per cent while meat and fish segment also witnessed a rise of 11.34 per cent and egg prices too rose 11.13 per cent. Vegetable prices however, slipped -6.27 per cent on-year in February. The government has mandated the central bank to keep retail inflation within the range of 4 per cent with a margin of 2 per cent on either side. The retail inflation data is primarily factored in by the RBI while making its bi-monthly monetary policy. In parallel, India’s factory output or IIP witnessed a contraction of (-)1.6 per cent on-year to 135.2 during the month of January.
- Science and Technology - Space Hurricane - Scientists from China recently discovered a space hurricane for the first time ever above the North pole. Previously, it was believed, space hurricanes were a theoretical phenomenon. As per their report, the hurricane measured roughly 600 miles across and rained down charged electrons for as long as eight hours. The space hurricane spun counterclockwise at speeds up to 4,700 miles per hour, the academic paper reported. The hurricane was reported in space directly above the North Pole. The new finding could help scientists learn more about how the Sun affects Earth’s atmosphere, gathering more details on how space weather might harm satellites and other objects in orbit. Space Hurricane - They are thought to be a result of the solar wind and Earth’s magnetic field interacting. It is a huge, funnel-like, spiral geomagnetic storm that occurs above the polar Ionosphere of Earth, during extremely quiet conditions. They are related to the aurora borealis phenomenon, as the electron precipitation from the storm’s funnel produces gigantic, cyclone-shaped auroras. They are made up of plasmas, consisting of extremely hot ionized gases that rotate at extremely high speeds. Space hurricanes are caused by plasma unleashed from the sun as solar wind. These charged particle clouds travel through space and fuel magnetic storms as they interact with magnetic fields.
- Governance and Institutions - One Nation One Ration Card System - The ministry of finance has announced that 17 states have successfully implemented ‘one nation, one ration card system’ after Uttarakhand became the latest state to complete the operationalization of reforms. One Nation One Ration Card (RC) will ensure all beneficiaries especially migrants can access PDS across the nation from any PDS shop of their own choice. No poor person is deprived of getting subsidised foodgrains under the food security scheme when they shift from one place to another. It also aims to remove the chance of anyone holding more than one ration card to avail benefits from different states. This will provide freedom to the beneficiaries as they will not be tied to any one PDS shop and reduce their dependence on shop owners and curtail instances of corruption. A standard format for ration card has been prepared after taking into account the format used by different states. For national portability, the state governments have been asked to issue the ration card in bi-lingual format, wherein besides the local language, the other language could be Hindi or English. The states have also been told to have a 10-digit standard ration card number, wherein first two digits will be state code and the next two digits will be running ration card numbers. Besides this, a set of another two digits will be appended with ration card number to create unique member IDs for each member of the household in a ration card.
- Governance and Institutions - Expansion of Mid-day Meal Scheme - The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Education has recommended that all government schools start providing free breakfast in the coming academic year, as a part of an expansion of midday meal scheme envisaged by National Education Policy. The National Education Policy identifies “providing food and nutrition” as one of the key long-term thrust areas for financing to cultivate a robust education system. Research shows that the morning hours nutritious breakfast can be productive for the study of cognitively more demanding subjects and hence these hours may be leveraged by providing a simple but energizing breakfast in addition to midday meals. Challenges - Severe funding Crunch is likely to delay the scheme. The Centre's current expenditure on the Midday meals scheme is about 11000 crore. Free breakfast would involve an additional budget of 4000 crore but the School Education Department saw a budget cut of almost 5000 crore for the year 2020-21.
- Indian Economy - Licensing conditions for Telecom Companies amended - The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has amended licensing conditions for telecom companies. The new norms will be implemented from 15th June 2021. In March 2021, the Union Cabinet approved the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for the telecom sector to reduce imports and move towards self-reliance. To include defence and national security as parameters when purchasing ‘trusted telecom products’ and sourcing equipment from ‘trusted telecom equipment sources’. Telecom companies can use telecom products only from trusted sources in its network and must take permission from the designated authority (National Cyber Security Coordinator) if they plan to upgrade their existing network using telecom equipment that has not been designated as a trusted product. The new norms will not impact the annual maintenance contracts or upgrades to existing equipment already being used by the telcos in their networks. Trusted Telecom Products/Trusted Telecom Equipment Source: It is simply a product, a company, or a technology that has been deemed safe by the government of a nation for use in its crucial and critical infrastructure.
- Energy - India’s biggest floating solar power plant - India’s biggest floating solar power plant by generation capacity (100MW) is being developed by the National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPC) at Ramagundam in Peddapalli district of Telangana. The project is in line with India's commitment to attain the target of 175 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2022 including 100 GW of solar installed capacity. It refers to the deployment of photovoltaic panels on the surface of water bodies. They are a viable alternative to land-based solar arrays with applications in India. There are a large number of major reservoirs in the Southern Region which provides a huge opportunity to go for renewable energy in the floating solar method. The thermal plant at Ramagundam would be one of the renewable (solar) energy plants being developed by NTPC with an installed capacity of 447MW in the Southern Region and the entire capacity would be commissioned by March 2023. The renewable energy plants that are likely to be commissioned in the next three months are 25MW floating solar plant at Simhadri thermal power plant near Visakhapatnam and 92MW floating solar plant at Kayamkulam in Kerala.
- World Economy - Bitcoin shines, again - Bitcoin prices crossed $57,000-mark for the first time in over two weeks on Thursday (11-03-2021) after the US House of Representatives passed a COVID-19 relief package worth $1.9 trillion, including $1,400 stimulus checks. The world's largest cryptocurrency had hit a record high of $58,350 on February 21 before witnessing a slump. Bitcoin currently has a market value of over $1 trillion. The crypto asset has seen wild swings lately, leading to questions on sustainability of its entire model.
- Indian Economy - Finance Ministry asks SEBI to withdraw bond rule - The Finance Ministry has asked the SEBI to withdraw the new regulation that requires treating perpetual bonds as 100-year maturity debt papers for the purpose of valuation. The ministry stated that the "clause on valuation was disruptive in nature". The SEBI directive was part of a wider circular on prudential limits for mutual fund investments in AT-1 bonds. The SEBI had asked that these be valued as 100-year bonds. The directive, due to kick-in from Apr.1, 2021, was part of a wider circular on prudential limits for mutual fund investments in AT-1 bonds. Objecting to the valuation norms prescribed, the Department of Financial Services (DFS) felt it could lead to large mark-to-market losses for mutual funds. No benchmark exists for 100-year bonds, and mutual funds could see large swings in the net asset value of units and this could lead to panic redemption in these securities. Additionally, capital raising by PSU banks will be adversely impacted and lead to increased reliance on the government for capital raising.
- [message]
- SECTION 2 - DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- [message]
- 1. ECONOMY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Inflation rises, IIP shrinks
- March data release: The National Statistical Office (NSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the Quick Estimates of Index of Industrial Production (IIP) for January 2021 and Consumer Price Index (CPI) numbers for February 2021. Industrial production contracted unexpectedly in January after posting modest growth in the month before, data released by the government showed, underlining the fragile recovery that could be at risk from rising Covid-19 infections in key states.
- Inflation up: Separately released data showed retail inflation accelerated more than expected to a three-month high of 5.03% in February 2021, which may stoke concerns of a further rise in bond yields and higher market interest rates.
- IIP situation: Industrial production contracted 1.6% in January against a 1.5% rise in December and 2.2% expansion in January 2020, with most key sectors reporting declines from a year ago. The contraction in IIP numbers at -1.6% for January 2021 comes as a bit of surprise after turning positive in December. The manufacturing sector continues to contract at 2% (showing) that India still has some distance to cover before the economy recovers. A Reuters poll had predicted a 0.9% rise in industrial production in January, backed by manufacturing, which has the highest weight in IIP. It posted a 2% decline in February while mining shrank 3.7%. Electricity generation was up 5.5%. Eighteen of the 23 sub-sectors of manufacturing contracted in January. Consumer durables production, an indicator of urban demand, declined 0.2%. Consumer non-durables shrank 6.8%.
- Sadly speaking: The major disappointment is negative growth in consumer goods, which was expected to be positive. The pent-up demand story has quite clearly paused as seen by these numbers. Capital goods production, an indicator of investment, shrank 9.6%, indicating that the anticipated investment revival is yet to manifest itself. "We remain circumspect regarding the intensity of the rebound in consumption immediately after the vaccine rollout widens, as some categories of households may choose to rebuild the savings that they had drained during the lockdown and post-lockdown period," said Aditi Nayar, principal economist, ICRA. In the April-January period of FY21, India's factory output shrank 12.2% compared with 0.5% growth in the year-ago period.
- The spoilers: India's economy is widely expected to post strong double-digit growth in FY22, but a Covid-19 resurgence, higher fuel and commodity prices and possibly likely firmer interest rates have emerged as risks to the recovery. Some cities in Maharashtra, which is seeing a spike in Covid-19 cases, have imposed lockdowns to contain the surge. The Indian economy expanded 0.4% in the December quarter to emerge from the pandemic-induced technical recession but is projected to shrink 8% in FY21.
- Inflation spike: Retail inflation, as measured by the consumer price index (CPI), had been easing for the last two months and had dropped to a 16-month low in January 2021. Despite the spike, retail inflation is still within the RBI's mandated target of 4% with a band of 2 percentage points on either side, but higher commodity prices remain a risk. Food and beverages firmed up to 4.25%, compared with a rise of 2.67% last month. Fuel and light inflation was 3.53% compared with 3.87% in January while household goods and services inflation rose to 3.07% from 2.8% and health inflation firmed up to 6.33% from 6.02%.
- Petrol on fire: Higher fuel prices have been passed through, reflecting an 11.36% increase in transport and communications inflation. Core inflation hardened to a three-month high 5.7% in February from 5.5% in the previous month, reiterating that an uptick in commodity prices, rising demand, and emerging pricing power will keep inflationary pressures intact. In Feb 2021, the monetary policy committee of the Reserve Bank of India unanimously retained the policy repo rate at 4% while maintaining an accommodative stance to support the economy.
- Big change coming or not: This is the last set of retail inflation data before the central bank and the finance ministry announce a fresh inflation targeting framework. The central bank has favoured continuing with the current target. The higher inflation print could put further pressure on bond yields, which have already firmed up in line with the rise in the US and other major economies. The monetary policy committee will meet on April 5-6, 2021.
- [message]
- 2. ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper
Goa’s draft CZMP
- Public unhappy: The draft Coastal Zone Management Plan of Goa has met with criticism from the wider sections of the society.
- History: In 2011, Union Ministry for Environment aimed to secure the livelihood of fishing and other local communities living in the coastal areas. It also wanted to conserve and protect coastal stretches, their unique environment and marine area and promote development in a sustainable manner. Hence the CRZ notification was formulated in 2011. It declared the coastal stretches of India and its territorial waters, excluding Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands, as Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ). It restricted the setting up and expansion of any industry, operations or processes and manufacture or handling or storage or disposal of hazardous substances there. Then the respective state governments and UT’s were directed to prepare CZMP by identifying and classifying the CRZ areas.
- What action did Goa take: It is India’s smallest state with a 105 km coastline. The state environment department directed the National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management to prepare the CZMP. The National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management (NCSCM) is an agency approved by the Centre located in Chennai. Its draft report stated that the proposed actions present in the CZMP will be implemented by administrative or other public authorities and by the private sector. The plan aimed to address the priority management issues in the coastal zone over a defined implementation period.
- Why criticised: The draft plan provided only 30-day limit for inviting suggestions and objections to the draft from the public. This is contrary to the 60-day limit provided by the Environment Protection Rules, 1986. Environmental activists question the state government’s intention of fixing only one day to decide the plan for the entire coastline of Goa. It is also alleged that several errors are reported in the draft CZMP and they are:
- Re-zoning of beach areas are carried out without any legal basis
- The maps are put for public hearing without examining the errors pointed out by village communities earlier
- Several illegal constructions are allowed in the draft which indicates there is an indirect influence on its preparation
- Locals and fishermen claim that some homes, villages, municipal areas and churches are left out in the CZMP
- [message]
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Significance of India-Bangladesh Transport Connectivity: World Bank
- Cooperation will be good: A World Bank report named “Connecting to Thrive: Challenges and Opportunities of Transport Integration in Eastern South Asia” stated that seamless transport connectivity between India and Bangladesh has the potential to increase national income by as much as 17% in Bangladesh and 8% in India. The report analyzes the Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) Motor Vehicles Agreement (MVA).
- Points to note: The key issues are -
- Trade - Bilateral trade accounts for only about 10% of Bangladesh’s trade and a mere 1% of India’s trade. In East Asian and Sub-Saharan African economies, intraregional trade accounts for 50% and 22% of total trade, respectively. High tariffs, para-tariffs, and nontariff barriers also serve as major trade barriers. Simple average tariffs in Bangladesh and India are more than twice the world average.
- Difficulty in crossing border - Weak transport integration makes the border between Bangladesh and India thick. Crossing the India–Bangladesh border at Petrapole–Benapole, the most important border post between the two countries, takes several days. In contrast, the time to cross borders handling similar volumes of traffic in other regions of the world, including East Africa, is less than six hours.
- (Isolated North-East - Indian trucks are not allowed to transit through Bangladesh. As a result, the northeast of India is particularly isolated with the rest of the country and connected only through the 27-km-wide Siliguri corridor, also called the “chicken’s neck”. This leads to long and costly routes.
- Benefits of better connectivity:
- Increased real income - All districts in Bangladesh would benefit from integration, with the eastern districts enjoying larger gains in real income. States bordering Bangladesh such as Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Tripura in the northeast, and West Bengal on the west, and states further away from Bangladesh such as Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra would also gain huge economic benefits from seamless connectivity.
- Increased exports - Will yield a 297% increase in Bangladesh’s exports to India and a 172% increase in India’s exports to Bangladesh.
- Strategic importance - Geographically, Bangladesh’s location makes it a strategic gateway to India, Nepal, Bhutan, and other East Asian countries. Bangladesh can also become an economic powerhouse by improving regional trade, transit and logistics networks.
- Important recommendations: The report suggested that
- Strengthen the MVA - Harmonizing driver’s licensing and visa regimes. Establishing an efficient regional transit regime. Rationalizing and digitizing trade and transport documents. Liberalizing the selection of trade routes.
- Improving regional connectivity - Expand the effective capacity of core transport and logistics infrastructure along regional corridors. Ensure competition in transport service markets. Deploy modern information technology infrastructure at land ports and seaports. Develop off-border custom clearance facilities in Bangladesh and India.
- Integration of local communities - Connecting local markets to regional corridors. Removing logistics bottlenecks in export-oriented value chains. Improving women’s participation in export-oriented agricultural value chains at the macro, community, and household levels.
- Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal Motor Vehicles Agreement: The BBIN is "Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal (BBIN) Initiative", a sub-regional architecture of countries in Eastern South Asia, a sub-region of South Asia. It meets through the official representation of member states to formulate, implement and review quadrilateral agreements across areas such as water resources management, connectivity of power, transport, and infrastructure.
- MVA - It was signed on 15th June 2015 in Thimphu, Bhutan, and seeks to facilitate the unrestricted cross-border movement of cargo, passenger, and personal vehicles between BBIN countries. As per the agreement, member countries would allow vehicles registered in the other countries to enter their territory under certain terms and conditions. Customs and tariffs will be decided by the respective countries and these would be finalised at bilateral and trilateral forums. Implementation of the MVA has been delayed as the countries work to clarify some of the provisions that are supposed to be elaborated in protocols.
- Objective - To provide seamless people-to-people contact and enhance economic interaction by facilitating cross border movement of people and goods.
- [message]
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
Expansion of Mid-day Meal Scheme
- NEP suggest: The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Education has recommended that all government schools start providing free breakfast in the coming academic year, as a part of an expansion of midday meal scheme envisaged by National Education Policy. The National Education Policy identifies “providing food and nutrition” as one of the key long-term thrust areas for financing to cultivate a robust education system.
- Points to note: Research shows that the morning hours nutritious breakfast can be productive for the study of cognitively more demanding subjects and hence these hours may be leveraged by providing a simple but energizing breakfast in addition to midday meals.
- Challenges: Severe funding Crunch is likely to delay the scheme. The Centre's current expenditure on the Midday meals scheme is about 11000 crore. Free breakfast would involve an additional budget of 4000 crore but the School Education Department saw a budget cut of almost 5000 crore for the year 2020-21.
- Midday Meal Scheme (MDM): The Midday meal scheme (under the Ministry of Education) is a centrally sponsored scheme which was launched in 1995. It is the world’s largest school meal programme aimed to attain the goal of universalization of primary education. It provides cooked meals to every child within the age group of six to fourteen years studying in classes I to VIII who enrolls and attends the school.
- Objective: It addresses hunger and malnutrition, increases enrolment and attendance in school, improves socialisation among castes, provides employment at grassroot level especially to women.
- Quality check: AGMARK quality items are procured, tasting of meals by two or three adult members of the school management committee. If the Mid-Day Meal is not provided in school on any school day due to non-availability of food grains or any other reason, the State Government shall pay food security allowance by 15th of the succeeding month.
- Regulation: The State Steering-cum Monitoring Committee (SSMC) oversees the implementation of the scheme including establishment of a mechanism for maintenance of nutritional standards and quality of meals.
- Nutritional standards: Cooked meal having nutritional standards of 450 calories and 12 gm of protein for primary (I-V class) and 700 calories and 20 gm protein for upper primary (VI-VIII class)
- Coverage: All government and government aided schools, Madarsa and Maqtabs supported under the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).
- Issues and challenges:
- Corruption - There have been instances of plain chapatis being served with salt, mixing of water in milk, food poisoning etc.
- Caste bias and discrimination - Food is central to the caste system, so in many schools, children are made to sit separately according to their caste status.
- Covid-19 - The pandemic posed serious threats to children and their health and nutritional rights. The nationwide lockdown has disrupted access to essential services, including Mid-Day Meals.
- Menace of malnutrition - According to the National Family Health Survey-5, several states across the country have reversed course and recorded worsening levels of child malnutrition. India is home to about 30% of the world’s stunted children and nearly 50% of severely wasted children under the age of five.
- Global Nutrition Report-2020: As per the Global Nutrition Report 2020, India is among 88 countries that are likely to miss global nutrition targets by 2025.
- Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2020: India has been ranked at 94 among 107 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2020. India has a level of hunger that is “serious”.
- Summary: Children will be unable to learn optimally when they are undernourished or unwell. Hence, the nutrition and health (including mental health) of children will be addressed, through nutritional breakfast including mid day meals. This expansion would further help to stop hunger from keeping children away from schools and to improve enrolment.
- [message]
- 5. POLITY AND CONSTITUTION (Prelims, GS Paper 2, GS Paper 3)
Forest Rights Act in J&K
- The story: The Jammu & Kashmir government's decision to implement the Forest Rights Act is a cause of concern.
- What is Forest Rights (FRA) Act: It provides Adivasis access and ownership rights, forest-based livelihood rights, and minor forest produce rights.
- How is FRA implemented: The forest rights committees will assess the nature and extent of rights being claimed at the village-level. Then, these claims would be scrutinised by the sub-divisional committees which will then prepare a record of forest rights. District-Level Committees will give the final approval and grant forest rights.
- Why a concern: On October 31,the J&K government’s decided to declare State Land (Vesting of Ownership to the Occupants) Act, 2001, also known as the Roshni Act, null and void. This Act was struck down due to the questionable transfer of ownership of state land to many influential people, including Ministers, legislators, bureaucrats, and police officers. Some say that it provided ownership rights to many poor, landless Adivasis & now the land will be retrieved from them.
- In case of J&K, there is no cut-off date mentioned in the FRA unlike rest of India, where the act provides recognition of forest rights to forest dwellers who had occupied forest land before December 13, 2005.
- Without a cut-off date & declaring the Roshni Act null and void, will lead to forceful evictions & tribal families will not benefit from the implementation of the FRA.
- In the last few weeks, there was intensified eviction and demolition drives against nomads without any rehabilitation plans in place. Moreover Adivasis largely depend on non-tribal leadership to represent their issues and demands as they lack of political reservation leading to further marginalisation.
- Summary: Until November 2020, neither the Centre nor the Union Territory administration said a word about the FRA. Then, starting in mid-November, the government invoked the 94-year-old obsolete and outdated Indian Forest Act, 1927, and began issuing eviction notices to Gujjar tribals and other traditional forest-dwellers. Some gujjar huts in villages that are close to forests were also demolished. The 1927 law contradicts the FRA, and people also resisted being evicted in some places. After a hue and cry, the evictions became a political issue and former chief minister Mehbooba Mufti visited some affected villages. The forest department has asked tribal gujjars and other traditional forest-dwellers to surrender the forest land they have been living on for centuries. Let the people and officials of the forest, rural development, panchayati raj, land revenue and tribal affairs departments be trained and sensitised on the FRA. If the tribal affairs department does not have enough manpower for this at the district or block levels, then government teachers, ICDS employees, and other officials can be asked to join this department on deputation (for two years or longer), so that the FRA can be properly rolled out.
- [message]
- 6. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (Prelims, Various GS Papers)
International cooperation: ISRO
- India Japan space cooperation: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) reviewed cooperation in earth observation, lunar cooperation and satellite navigation.
- Points to note: Both agencies agreed to explore opportunities for cooperation in “space situational awareness and professional exchange programme”. They signed an Implementing Arrangement for collaborative activities on rice crop area and air quality monitoring using satellite data. India and Japan are already working on a joint lunar polar exploration (LUPEX) mission. The LUPEX aims to send a lander and rover to the Moon’s south pole around 2024.
- Agreements with other countries: India and Italy have decided to explore opportunities in earth observation, space science and robotic and human exploration. India and Australia signed an amendment to the MoU which will build on the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. Both are also in discussions for Australia to host vital tracking infrastructure to support the Gaganyaan manned space flight mission.
- Few achievements:
- Chandrayaan-1 - ISRO’s maiden mission to Moon, the Chandrayaan-1, has been an exemplary example of international cooperation with its international payloads. It has also earned several national and international laurels and was instrumental in the ISRO-NASA joint discovery of water molecules on the moon surface, unattained by any of the previous missions of such nature.
- Megha-Tropiques - The Indo-French joint satellite mission called MEGHA-TROPIQUES was launched in 2011 for the study of the tropical atmosphere and climate related to aspects such as monsoons, cyclones, etc.
- Saral - The Indo-French joint mission, named SARAL (Satellite for ALTIKA and ARGOS) for studying the ocean from space using altimetry was successfully launched in 2013.
- NISAR - ISRO and NASA are realizing a joint satellite mission called NISAR (NASA ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) for earth science studies. The mission will observe Earth and measure its changing ecosystem and masses globally. It is the world’s most expensive imaging-satellite and the two space agencies intend to launch the satellite by 2022.
- UNNATI - ISRO has launched capacity building programme on nano satellite development, named as UNNATI (UNispace Nanosatellite Assembly & Training by ISRO) as an initiative of UNISPACE+50 (the 50th Anniversary of the first United Nations conference on the exploration and peaceful uses of outer space).
- TRISHNA - ISRO and the French space agency CNES have partnered in developing advanced upgradation satellites like TRISHNA to monitor the water cycle to help in finding out proper ways to utilize it.
- [message]
- 7. SOCIAL ISSUES (Prelims, GS Paper 2)
Challenges faced by nomadic tribes
- Parliament informed: In a written reply in Rajya Sabha, the Minister of State for Social Justice and Empowerment stated that a Development and Welfare Board for Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DWBDNCs) was constituted for development and welfare of Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities in 2019. The welfare board was constituted for a period of three years extendable upto 5 years.
- Points to note: There are numerous challenges faced by nomadic tribes. There are nearly 1,500 nomadic and semi-nomadic tribes and 198 denotified tribes, comprising 15 crore Indians, according to the Renke Commission, 2008. These remain socially and economically marginalised even now, depriving many of them of basic human rights. The most pressing issue is of their identity.
- Lack of basic infrastructure - Facilities like drinking water, shelter, and sanitation facilities are not available to the communities. Healthcare and education facilities are also not available.
- Bad treatment by local administration - Due to the stigma of Criminals bestowed upon them in the past, they are still treated criminals and tortured by the local administration and police.
- Lack of social security cover - Since they are on move frequently, they do not have a permanent settlement. As a result, they lack social security cover and are not issued Ration Card, Aadhar Card, etc. and hence they are not getting benefits under the government welfare schemes. The caste categorization is not very clear for these communities, in some states some of the communities are included under the SC category, in some other states they are included under OBCs. However, most of the groups from these communities do not have caste certificates and hence are not able to avail the benefits of government welfare programs.
- DWBDNC's responsibilities: To formulate and implement Welfare and Development programmes, as required, for Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DNCs). To identify the locations/areas where these communities are densely populated. To assess and identify gaps in accessing existing programmes and entitlements and to collaborate with Ministries/implementing agencies to ensure that ongoing programmes meet the special requirements of DNCs. To monitor and evaluate the progress of the schemes of the Government of India and the States/UTs with reference to DNCs.
- Schemes for Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities:
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs - This Centrally Sponsored Scheme was launched in 2014-15 for the welfare of those DNT (Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes) students who are not covered under SC, ST or OBC. The income ceiling for eligibility is Rs. 2.00 lakh per annum. The scheme is implemented through State Governments/UT Administrations. The expenditure is shared between the Centre and the States in the ratio of 75:25. The scheme of Pre-matric Scholarship for DNT students is helpful in spreading education amongst DNT children especially the girl child.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Scheme of Construction of Hostels for DNT Boys and Girls - This Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in 2014-15, is implemented through State Governments/UT Administrations/Central Universities. The aim of the scheme is to provide hostel facilities to those DNT students; who are not covered under SC, ST or OBC; to enable them to pursue higher education. The income ceiling for eligibility is Rs. 2.00 lakh per annum. The Central Government provides a maximum of 500 seats per annum throughout the country. The expenditure is shared between the Centre and the States in the ratio of 75:25.
- Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities: The Denotified tribes are those that were notified under the Criminal Tribes Acts enforced during British Rule, whereby entire populations were branded criminals by birth. In 1952, the Act was repealed and the communities were de-notified. The Nomadic tribes maintain constant geographical mobility while semi-nomads are those who are on the move but return to fixed habitations once a year, mainly for occupational reasons. The distinction between nomadic and semi-nomadic do not involve distinguishable ethnic categories or social groups, it rather describes the degree of mobility practiced by them.
- [message]
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
PM addresses 4th Global Ayurveda Festival
- What it is: Prime Minister, Narendra Modi addressed the fourth Global Ayurveda Festival on March 12, 2021 in the virtual mode.
- Points to note: The PM highlighted the growing global interest in Ayurveda. He also appreciated the efforts of those working on Ayurveda across the globe. While highlighting the importance of Ayurveda as a holistic human science and its importance from plants to the plate of human, he highlighted how the demand for ayurvedic products is steadily rising amid the covid-19 pandemic.
- Virtual mode: The Fourth Global Ayurveda Festival was planned for 16th to 20th May 2020. However, because of Covid-19 pandemic it shifted to 2021 and is being organised in virtual mode from 12th to 19th March 2021. Even during the pandemic, the intended intensity, impact, size, and participation have not been diluted. The even would comprise of live sessions such as plenaries, parallel sessions, symposiums, virtual exhibition, paper presentations and virtual networking.
- Theme of the festival: International Ayurveda Seminar will be organised under the Theme “Strengthening Host Defence System – Ayurveda A Potential Promise”; International Delegate Assembly will be organised under the Theme “Globalizing Ayurveda – Scope, Challenges and Solutions” while the “International Business Meet” will be organised under the Theme “Global Ayurveda Pharmacy – Practices, Possibilities and Policies”.
- Awards: The National Academy of Letters have announced the names for the “Sahitya Akademi Award 2020 on March 12, 2021. The names were announced during the opening of annual “Festival of Letters” event.
- Highlights:
- The award will be bestowed upon the politician-writer M Veerappa Moily, poet Arundhathi Subramaniam along with other 20 writers. Subramaniam have won the award for her poetry collection called “When God is a Traveller” in English. Veerappa Moily has been named for his epic poetry called “Sri Bahubali Ahimsa Digvijayam” in Kannada language. The list comprises of seven books of poetry, five short stories, four novels, two plays, and one memoir and one epic poetry in 20 Indian languages. The awards for Nepali, Malayalam, Odia and Rajasthani Languages will be announced later.
- Other Awardees - In the “Poetry Category” the award was bestowed upon Harish Meenakshi (Gujarati), RS Bhaskar (Konkani), Anamika (Hindi), Irungbam Deven (Manipuri), Nikhileshwar (Telugu) and Rupchand Hansda (Santali). In the “Novel Category” Imaiyam (Tamil), Nanda Khare (Marathi), Mahesh Chandra Sharma Gautam (Sanskrit), and Sri Hussain-ul-Haque have been named as winner. While, Apurba Kumar Saikia (Assamese), Hiday Koul Bharti (Kashmiri), Dharanidhar Owari (Bodo),Gurdev Singh Rupana (Punjab) and Kamakant Jha (Maithili) have won the award for short stories.
- Selection procedure - These books were selected following the recommendations made by a jury of three members of the concerned languages. They made their final decision in accordance with the procedure which was set down for this purpose. Under it, the Executive Board declared the Awards based on unanimous selections made by jurors or selection made in accordance with the majority vote.
- Sahitya Akademi Award: It is a literary honour in India, conferred by Sahitya Akademi which is India’s National Academy of Letters. The award is conferred to the most outstanding books of literary merit which is published in any 24 major Indian languages including Hindi, English and other 22 languages of the Eighth Schedule of Constitution. The award includes a casket comprising of an engraved copper plaque, a shawl and amount of Rs 1,00,000.
- The story: The foreign secretary of India stated on March 12, 2020 that the Leaders of the United States, India, Australia and Japan have agreed to pool finance, manufacture and distribute the capacity in order to send 1 billion coronavirus vaccines across Asia and in the Indo-Pacific region to assist them by the year 2022.
- Key points: The “Quad” group comprising of four nations have the objective of expanding the global vaccinations in a counter to growing vaccination diplomacy of China in the Southeast Asia and across the world. Among the four countries in the Quad group, India is the largest vaccine maker across the world. This will help in speeding up the process of post pandemic recovery. This collaboration among the grouping will not impact the production of Vaccines for 1.4 billion people of India. Thus, the India’s formidable vaccine production capacity will further be expanded with the help of US, Japan & Australia. This way, the Quad will be a positive force for achieving the global good and peace in the region.
- Nature of collaboration: Under the agreement, India will be using its manufacturing capacity in order to make U.S. vaccines. For that matter, the financing will be coming from U.S. International Development Finance Corporation and Japan Bank for International Cooperation. On the other hand, Australia will be financing the training. The country will also provide the last-mile logistical support to distribute the vaccines in the Southeast Asia, Pacific Islands and countries in across the Indian Ocean.
- Concerns: This initiative might be hampered because of the export restrictions provided by the United States on the critical raw materials which are required for vaccine supply chain of India. This is the only bilateral concern that exists between India and US with respect to the “QUAD Partnership on covid-19 vaccines”.
- A shocking note: All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has released the approval process handbook for academic year 2021-22. It highlights that Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics will continue to be important subjects for core streams of engineering such as mechanical engineering. However, for streams such as Textile Engineering, Agriculture or Biotechnology, students will be given an option of not studying these three subjects in class 12th. Those who does not opt for these subjects will have to make up through bridge courses in college.
- The rules: The rule is all set to be implemented from the academic year 2021-22. As per the rule, the students who are seeking admission to certain engineering courses like Textile engineering etc will have to pass 10+2 by taking any of the three subjects out of Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics, Electronics & IT, Computer science, Technical Vocational Subject, Information practices, Biotechnology, Agriculture, Engineering and Business studies. The new rule also mandates that, the unreserved category students will have to score 45% marks and the reserved category should score 40% marks in order to pass the class 12th level.
- Alternatives suggested: Since Maths, physics and Chemistry will not be compulsory for students of class 12 to opt for streams like Textile engineering, Agriculture or Biotechnology, so the AICTE has suggested to introduction a bridge courses in maths and physics in the engineering colleges in order to strengthen base of these subjects in initial semesters for the students coming from diverse backgrounds.
- AICTE: The AICTE is a statutory body and a national-level council for the technical education. It works under the Department of Higher Education. The council was set up in the month of November 1945. It was earlier an advisory body. The council was given the statutory status in the year 1987 by an Act of Parliament.
9.1 Today's best editorials to read
- We offer you 7 excellent editorials from across 10 newspapers we have scanned.
- [message]
- SECTION 3 - MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)