Useful compilation of Civil Services oriented - Daily Current Affairs - Civil Services - 24-02-2021
- Healtchare and Medicine - Flesh-eating disease spreading in Australia - A flesh-eating disease is spreading in parts of Australia, with Victoria's Health Department issuing a warning. Cases of 'Buruli ulcer' were identified in the Melbourne suburbs of Essendon, Moonee Ponds and Brunswick West. "Early diagnosis is critical to prevent skin and tissue loss...Buruli ulcer must be notified to the department within five days of diagnosis," the authorities said. Buruli ulcer is a disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium ulcerans, that affects the skin but can also affect the bone. Cases are generally seen in the tropics, primarily in West Africa and Australia. Infection often leads to ulcers on the arms or legs, which can also destroy skin or soft tissue. Treatment involves antibiotics. Left untreated, it can lead to permanent disfigurement and disability.
- Science and Technology - DRDO launches Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile - The Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) in Feb 2021 conducted two successful launches of the indigenously designed and developed Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VL-SRSAM). The missile is capable of neutralizing various aerial threats at close ranges including sea-skimming targets. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh congratulated DRDO on the successful trials. Indigenously designed and developed by DRDO for the Navy, the VL-SRSAM is meant for neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges, including sea-skimming targets. The launches were carried out for demonstration of vertical launch capability as part of its maiden launch campaign.
- Science and Technology - Panorama of Mars from Perseverance rover released - NASA released the first panorama of Mars showing Perseverance rover's landing location. The panorama, taken by the Navigation Cameras or Navcams aboard Perseverance rover, was stitched together from six individual images after they were sent back to Earth. The Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover will search for signs of ancient microbial life, which will advance NASA's quest to explore the past habitability of Mars. The rover has a drill to collect core samples of Martian rock and soil, then store them in sealed tubes for pickup by a future mission that would ferry them back to Earth for detailed analysis. Perseverance will also test technologies to help pave the way for future human exploration of Mars. Future human expeditions to Mars will be helped by all this, including finding ways to produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, identifying other resources (such as subsurface water), improving landing techniques, and characterizing weather, dust, and other potential environmental conditions that could affect future astronauts living and working on Mars.
- World Economy - Bitcoin suffers biggest daily drop - Bitcoin, the world's biggest cryptocurrency, suffered its biggest daily drop in a month on 22-02-2021 by falling as low as $45,000. The drop extended a slump of nearly a fifth from a record high of $58,354 hit two days ago. Bitcoin remains up around 60% for 2021. Ether also dropped more than 17%. This massive shakeout has again confirmed the fears of many that these currencies won't be stable for regular use and transactions. Big bull Rakesh Jhunjhunwala has asked Indian govt. to completely ban the cryptocurrency market in India. Tesla's Elon Musk has spoken for cryptos, and also cautioned against sharp price rise.
- Governance and Institutions - Centre aims to eliminate tuberculosis by 2025 - Prime Minister said on February 23, 2021 that the Central government is aiming to eliminate tuberculosis (TB) from the country by 2025. He said this while addressing a webinar on the health sector's budget implementation. He said that wearing masks, early diagnosis and treatment are important in its prevention. As per the annual TB report 2020 released in June 2020, around 24.04 lakh TB patients were notified in 2019, which amounts to a 14 per cent increase in TB notification as compared to 2018.The Prime Minister added saying that the Centre is not only investing in healthcare but also focusing on bringing in employment opportunities. TB is a serious infectious bacterial disease that mainly affects the lungs. The bacteria that cause TB are spread when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and most people infected with the bacteria that cause tuberculosis don't have symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they usually include a cough (sometimes blood-tinged), weight loss, night sweats and fever. Treatment isn't always required for those without symptoms. Patients with active symptoms will require a long course of treatment involving multiple antibiotics.
- Governance and Institutions - Intensified Mission Indradhanush 3.0 Launched - The Central Government initiated the IMI 3.0 program, which aims to provide free immunizations for pregnant women and children in India. The Union Health Minister, Dr. Harsh Vardhan, launched the Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) 3.0. The mission will be divided into two rounds. The first phase started on February 22, 2021, and the second phase on March 22, 2021. It will spread across 250 districts or urban areas in 29 States or Union Territories. In addition, the Minister also launched the IMI 3.0 portal and issued Operational Guidelines for it. He also launched promotional materials or IEC packages developed under the campaign.
- People and Personalities - Super 30 Founder Anand Kumar's work praised in Canada - A Canadian MP praised 'Super 30' Founder and educator Anand Kumar's "inspiring work". Giving an account of education projects in the Canadian Parliament, Marc Dalton said the Bihar-born's work is "helping students from underprivileged sections of society overcome all obstacles to reach premier institutions of India." Dalton also said Biju Mathew, of Maple Ridge, has written a book on Kumar. His life and work are portrayed in the 2019 film, Super 30, where Kumar is played by Hrithik Roshan. Anand Kumar was born in Bihar, India.
- Indian Politics - Covid cases rising again in some states - Union Health Ministry wrote to five states, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir and Chhattisgarh, where COVID-19 cases are rising and asked them to speed up the vaccination process. "It is advised...vaccination of healthcare and front line workers is expedited so as to confer immunity [soon]...they are also involved in containment...of COVID-19 cases," the Centre wrote. The object of expediting the vaccination process is to confer immunity in the shortest possible time frame to combat the rising trend of COVID-19 cases and positivity rate in some districts. India on 22-02-2021 reported 10,584 new coronavirus cases, taking the tally to 1,10,16,434. The death toll increased by 78 to 1,56,463. Maharashtra has been recording over 6,000 fresh COVID-19 cases for the last few days, sparking fears, and bringing new lockdowns.
- Indian Politics - Modi stadium the largest - President Kovind inaugurated the world's largest cricket stadium in Ahmedabad, and named it after Narendra Modi. The Motera Cricket Stadium, world's largest, was inaugurated in presence of Home Minister Amit Shah and Sports Minister Kiren Rijiju. The stadium boasts a capacity of 1,10,000. President Kovind perfomed 'Bhumi Pujan' of the Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Sports Enclave.
- Environment Ecology and Climate Change - US and Canada for zero net emissions - Following a bilateral meeting with Canadian PM Justin Trudeau, US President Joe Biden said that both the countries have agreed to work towards achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Biden said US was launching a "climate-ambition ministerial" and would align our policies to achieve this goal. US climate envoy John Kerry and Canada's Environment Minister Jonathan Wilkinson will host the ministerial. Carbon neutrality refers to achieving net zero carbon dioxide emissions by balancing carbon dioxide emissions with removal or simply eliminating carbon dioxide emissions altogether.
- [message]
- SECTION 2 - DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- [message]
- 1. ECONOMY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Welcome back China, let's do business
- Facts on the ground: China has regained position as India’s top trade partner in 2020, as India's reliance on imported machines outweighed its efforts to curb commerce with it after a bloody border conflict. Two-way trade between the longstanding economic and strategic rivals stood at $77.7 billion in 2020, according to data from India’s commerce ministry. That was lower than the previous year’s $85.5 billion total, but was enough to make China the largest commercial partner displacing the U.S. The India US bilateral trade with whom was $75.9 billion amid muted demand for goods in the middle of a pandemic.
- Hit China: Indian government banned hundreds of Chinese apps, slowed approvals for investments from the neighbor and called for self-reliance after a the deadly clash on LAC, but India continued to rely heavily on Chinese-made heavy machinery, telecom equipment and home appliances. As a result, the bilateral trade gap with China was at almost $40 billion in 2020, making it India’s largest.
- Total imports from China at $58.7 billion were more than India’s combined purchases from the U.S. and the U.A.E, which are its second- and third-largest trade partners, respectively. Heavy machinery imports accounted for 51% of India’s purchases from its neighbor.
- But India did manage to lower imports from China amid demand disruptions caused by the coronavirus pandemic. It also managed to increase its exports to China by about 11% from 2019 to $19 billion in 2020, which makes any further worsening of ties with Beijing a threat to New Delhi’s export revenue.
- Manufacturing: The tense relations are already weighing on India’s ambitions to bolster its manufacturing capabilities. India was slow to issue visas to Chinese engineers needed to help Taiwanese companies set up factories under a so-called production-linked incentive program, or PLI, to promote local manufacturing. Experts say the PLI schemes will take at least four-five years to create fresh capacities in specific sectors. Till then reliance on China would continue.
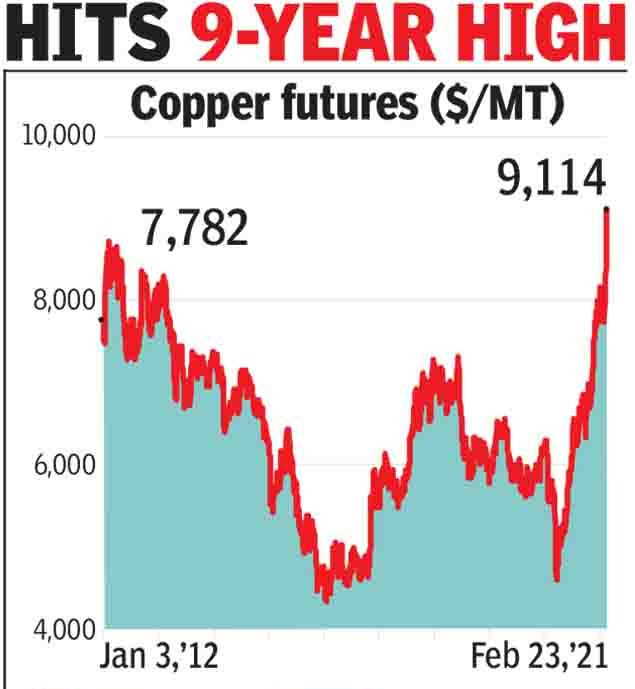
Copper prices will push India's import bill could by 35% in 2021
- Copper on fire: A combination of factors record high copper prices coupled with aggressive buying by China and the largest copper smelter in India remaining shut for the second year in a row will make copper imports 35% more costly in 2021.
- Facts: The LME copper prices touched nine years high in January 2021 to average $7,961 per tonne. Prices have touched the highest level since 2012 due to supply crunch of copper concentrates caused by disruptions in mining operations due to Covid-19 challenges amidst rising demand. The on-going concentrate supply issues and strong demand, particularly from China, is expected to keep copper prices elevated over the next quarter before the supply issues get resolved in 2021. Refined copper production fell by a sharp 24.4% to 231.7 thousand tonnes during Apr-Dec FY21 compared with Apr-Dec FY20 as the Covid-induced lockdown that brought business activities to a sudden halt.
- Importers to be hit: Refined copper prices are expected to average $6,500-6,800 per tonne in FY21 vs $5,923 in FY20, thereby impacting import dependent countries. India could spend up to 30-35% more just to import the same level of refined copper.
- Domestic situation: The domestic copper industry is operating at almost half of its capacity since the last two financial years due to closure of Vedanta four lakh tonnes a year copper smelter at Tuticorin. India will continue to be a net importer of copper in FY21, pending the resumption of Vedanta’s copper smelting facility. Imports will be lower in FY21 vs FY20 due to fall in domestic demand in first half of FY21. (all data based on experts' analyses)
- Where used: As per ministry of mines, the share of electrical and telecommunication industry in total consumption of copper is 56%, followed by transport (8%), consumer durables (7%), building & construction (7%), general Engineering goods (6%) and other industries including process industries (16%).
- [message]
- 2. ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper
Carbon Watch App – Chandigarh
- Watching the carbon: Chandigarh became the first state or Union Territory in India to launch Carbon Watch, a mobile application to assess the carbon footprint of an individual. Carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases — primarily carbon dioxide (or measured in CO2 equivalent) — released into the atmosphere by a particular human activity.
- Points to note:
- About the App - It focuses on individuals’ actions and calculates carbon footprint on the basis of Transport, Energy, Waste and Water consumption. It will also provide information such as the national and world average of the emission, and the individual’s level of emission generation. It encourages people to be Climate-Smart Citizens while making them capable of accessing their carbon footprint, along with providing them with steps to reduce it. It also sensitizes people about their lifestyle emissions, their impact and possible countermeasures to mitigate the same.
- Carbon Footprint - According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a carbon footprint is a measure of the impact people’s activities have on the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) produced through the burning of fossil fuels and is expressed as a weight of CO2 emissions produced in tonnes. It is usually measured as tons of CO2 emitted per year, a number that can be supplemented by tons of CO2-equivalent gases, including methane, nitrous oxide, and other greenhouse gases. It can be a broad measure or be applied to the actions of an individual, a family, an event, an organization, or even an entire nation.
- Carbon Footprint vs Ecological Footprint - Carbon footprint is different from ecological footprint. While the carbon footprint measures the emission of gases that contribute to global warming, the ecological footprint focuses on measuring the use of bio-productive space.
- Effects of Higher Carbon Footprint - Climate change is the ultimate effect of large carbon footprints. Greenhouse gases, whether natural or human-produced, contribute to the warming of the planet. From 1990 to 2005, carbon dioxide emissions increased by 31%. By 2008, the emissions had contributed to a 35% increase in radiative warming, or a shift in Earth’s energy balance toward warming, over 1990 levels. According to World Meteorological Organization (WMO) records, 2011-2020 was the warmest decade on record, in a persistent long-term climate change trend.
- Depletion of Resources - Large carbon footprints deplete resources on large scales, from a country’s deforestation activities to one home’s increased use of air conditioning.
- Methods of Reducing Carbon Footprint - Adopting the 4 R approach of "Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle" is useful. Driving more-efficient vehicles (or making sure that current vehicles are properly maintained), and taking public transportation, helps. Individuals and companies can also offset some of their carbon dioxide emissions by purchasing carbon credits, the money from which can go into projects such as planting trees or investing in renewable energy. Implementation of the Climate change conventions like the Paris Agreement and Indian initiatives for the same must be fast forwarded.
- Indian initiatives: India has been active on climate change efforts for some time now. Initiatives include Nation Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), National Wetland Conservation Programme, etc. As a member of the Paris Climate accord, India has urged the Western world to step up their contributions.
- [message]
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Dalai Lama’s reincarnation plans
- Who is the Dalai Lama: For the West, the Dalai Lama is a Nobel Peace Prize winner. For Tibetans, he’s a spiritual leader. But for the Chinese government, he’s a “wolf in monk’s robes” and a “splittist.” Those insults have sped up since December 2020, when it was reported that the contentious omnibus U.S. spending bill included a peculiar provision: the Tibetan Policy and Support Act of 2020 (TPSA). The Chinese Communist Party claims ultimate control over Tibetan souls.
- What is the new law: Introduced to their respective legislative bodies by Democratic Rep. James McGovern and Republican Sen. Marco Rubio, the TPSA supplants the similarly bipartisan Tibetan Policy Act of 2002. The new act is an overdue update. It covers a range of issues, including emphasizing environmental protection of the fragile Tibetan plateau, which is often referred to as the Third Pole because of its massive ice fields; encouraging the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights for American businesses engaged in Tibet; conditioning the establishment of new Chinese consulates in the United States on an establishment of a U.S. consulate in Lhasa; and acknowledging the role of the Central Tibetan Administration. The most politically significant provision is the assertion that the Dalai Lama’s reincarnation process should be left solely to the Dalai Lama’s and Tibetan Buddhist community’s wishes, and that Chinese officials who interfere in the process will face Magnitsky sanctions.
- China hurt badly: That strikes at the core of one of Beijing’s political-theological claims over Tibet; the argument, repeatedly made by Chinese officials, that only the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), cast as the legitimate successor of earlier dynasties, can determine the Dalai Lama’s successor. In the same way as China claims that its territorial boundaries are defined by the furthest reach of the Manchu-ruled Qing Empire, it argues that it is the successor of the role that Qing emperors, looking to legitimize their own relationship with Buddhism, played in recognizing Tibetan leaders.
- New law, and Chinese reactions: So the TPSA became the new main legislative measure guiding U.S.-Tibet policy. China quickly admonished the US for interfering with China’s “internal affairs.” It cited the CCP’s Measures on the Management of the Reincarnation of Living Buddhas, otherwise known as State Religious Affairs Bureau Order No. 5, to justify China’s outrage. The CCP in 2007 issued the “Order No. 5,” a decree that dictates that Buddhist temples must file a reincarnation application and obtain approval from several government agencies for upcoming reincarnations—all in the name of protecting religious freedom. China demonstrated further insecurity when the Chinese Embassy in India, inflamed by the triumphant Indian media coverage of the TPSA, sourly accused the Indian media of advocating the new act.
- Over centuries: The dalai lama lineage spans centuries, but the power and status of the role exponentially increased through formal relationships between Mongol rulers beginning around the 16th century. Through these alliances, both parties found mutual benefits; the dalai lama gifted Mongol rulers culture and prestige, and the Mongol rulers allowed the dalai lama to amass political clout in Tibet.
- The Great Fifth: The fifth Dalai Lama, known as “The Great Fifth,” oversaw the construction of the Potala Palace and the consolidation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. In the power struggles among the clashing empires of the Qing dynasty and Central Asian leaders in the 18th century, the seventh Dalai Lama was established as the head of the Tibetan government. Manchu ambans — an official role somewhere between regional commissioners and ambassadors — were stationed across Tibet. When the Qing dynasty collapsed in the early 20th century, the 13th Dalai Lama expelled the Manchu observers and formally declared Tibetan independence.
- The 1950s: The hesitance of Great Britain, India, and Russia to fully recognize Tibet as an independent government helped embolden China to invade Tibet in the 1950s. The powerful monastic community, determined to prioritize the cultivation of Tibetan Buddhism and their own power, eschewed the creation of a Tibetan military. So when the People’s Liberation Army stormed in from eastern Tibet to Lhasa, the imbalance was palpable. Tibet’s status rapidly deteriorated—under duress, the 14th Dalai Lama’s representatives signed off Tibet’s de facto independence in China via Mao Zedong’s Seventeen-Point Agreement, a document that promised religious freedom, the authority of the dalai lama, and gradual CCP reforms. And Mao quickly broke all promises!
- Revolt: Tibetans resented their loss of freedom, and it led to the massive 1959 uprising, when Tibetans gathered around the Dalai Lama’s palace and loudly called for Tibet’s independence. The escalating violence concerned the Dalai Lama and his advisors. After consulting with an oracle, the young Dalai Lama fled Tibet and into exile in India. Though the CCP disparages the Dalai Lama as a “splittist,” he and his representatives have repeatedly and explicitly stated that they merely desire self-determination for Tibetans in Tibet while remaining under China’s rule. The Dalai Lama’s representatives have met with Chinese representatives nine times. But in the face of preconditions imposed by the CCP, such as the requirement that the Dalai Lama “admit” that Tibet has always been an integral part of China, a stalemate has ensued.
- Who next: In the past few years, many have speculated on the Dalai Lama’s next reincarnation, or whether he would have one at all. The Dalai Lama is currently 85, but has promised he will try to live as long as 113 years, a particular age prophesied by an 18th-century lama. The Dalai Lama has stated that the next reincarnation will likely be born outside of Tibet, and may be a female. At the 14th Tibetan Religious Conference in November 2019, Tibetan religious leaders and representatives of the major schools of Tibetan Buddhism adopted a unanimous resolution urging the Dalai Lama to continue the reincarnation tradition. The Chinese government will try to appoint a puppet dalai lama. The Dalai Lama has not been the first major Buddhist figure whom the CCP has tried to co-opt — the Chinese government kidnapped Gedhun Choekyi Nyima, the 11th Panchen Lama (a lama rank that is only second to the Dalai Lama’s), when he was just 6 years old in 1995. His whereabouts today are unknown! The Chinese government’s replacement Panchen Lama serves as a saccharine figurehead, and Buddhists have rejected his appointment.
- US support: The U.S. government’s support for the TPSA is profound for Tibetan Americans, and that sentiment also resonates for Buddhists at large and non-Buddhists around the globe. Time and time again, Tibetans have unwillingly become the canary in the coal mine of Chinese totalitarianism; the U.S. government’s decision to emphatically support the Dalai Lama’s true reincarnation process exemplifies solidarity that should be replicated by other countries.
- [message]
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
Maharashtra ban on Coronil
- Baba's medicine banned: Home Minister of Maharashtra, Anil Deshmukh, said that sale of Coronil (Yoga guru Ramdev’s Patanjali group's medicine for Covid-19) will not be allowed in the state without proper certification from competent health organisations like WHO, IMA and others.
- Government stand: Deshmukh said that even the IMA questioned the said ‘clinical trials’ of Coronil & WHO refuted the false claims made by Patanjali Ayurveda for giving any certificate regarding its effectiveness for Covid19 treatment. Launching such a drug hurriedly and being endorsed by two senior Central Union Ministers is highly deplorable.
- Controversy: On February 19, Ramdev, at a press meet, said Coronil had received certification from AYUSH Ministry as a drug that can be used as “supporting measure in Covid-19” and as an immuno-booster. The press meet was attended by Union Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari and Union Health Minister Harsh Vardhan, a qualified doctor who is also chair of World Health Organization’s (WHO) Executive Board. The health minister said that during British colonial times, Ayurveda should have been recognised, its knowledge publicised, but India had to wait till Independence to do that.
- Patanjali said that “Coronil has received the Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product (CoPP) from the Ayush section of Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation as per the WHO certification scheme.” It called Coronil “an evidence-based medicine to fight Covid-19”. It claimed the drug can be exported to 158 countries.
- The WHO distanced itself from the product. Without taking names, WHO South-East Asia said it had not reviewed or certified the effectiveness of any traditional medicine for the treatment of COVID-19.
- False claims: Social media criticised Patanjali’s “false claims”, prompting CEO Acharya Balkrishna to clarify that their certificate had come from the Government of India, and not the WHO. "The WHO GMP compliant COPP certificate to Coronil is issued by DCGI, Government of India. It is clear that WHO do not approve or disapprove any drugs. WHO works for building a better, healthier future for people all over the world".
- WHO certification scheme: The WHO does not “approve or disapprove” drugs. It says its role in the area of medicines regulatory support is two-fold. One aspect relates to the development of internationally recognised norms, standards and guidelines. The second aspect relates to providing guidance, technical assistance and training in order to enable countries to implement global guidelines to meet their specific medicines regulatory environment and needs. Its certification scheme is for finished pharmaceutical products, and is a voluntary agreement among various countries. The scheme is an “administrative instrument that requires a participating Member State (a certifying country), upon application by a commercially interested party (the applicant company), to certify/attest to the competent authority of another participating Member State (the recipient country) that: "A specific pharmaceutical product is authorised for marketing in the certifying country, or if not, the reason why authorisation has not been accorded; The manufacturing facilities and operations conform to good manufacturing practices (GMP) as recommended by WHO.”
- What IMA said: The Indian Medical Association (IMA) had on February 22 criticised the “blatant lie of WHO certification” made by Panjali Ayurved, and demanded an explanation from Harsh Vardhan for endorsing it.
- “Being a Health Minister of the country, how justified is it to release such falsely fabricated unscientific product to people of the whole country and how ethical was it to promote the product in unethical, wrong and false ways,” the IMA statement said.
- The association also pointed out that as per the code of act of the Medical Council of India, no doctor can promote any drug, “whether for compensation or otherwise, any approval, recommendation, endorsement, certificate, report or statement” and said that it was “surprising that the Minister himself is promoting the drug (Coronil)”.
- The IMA then sought clarifications on the timeline for the clinical trial of Coronil, and what procedures were followed for the trials.
- Patanjali had claimed in 2020 also that Coronil could cure Covid-19, but the government had allowed it to sell the product only as an “immunity booster”. The company had claimed in June 2020 that its trials on “mild to moderately ill patients” were successful, and showed “100 per cent recovery of patients within seven days”.
- [message]
- 5. POLITY AND CONSTITUTION (Prelims, GS Paper 2, GS Paper 3)
Voice Vote in Indian Parliament not a good idea
- Voicing concern: The practice of resorting to voice vote and passing bills despite lack of a majority is increasing, and that may not be a healthy sign at all. The Karnataka Prevention of Slaughter and Preservation of Cattle Bill was passed by the State’s Legislative Council by voice vote in Feb 2021.
- How the Bill was passed: The law was passed by the Upper House despite the lack of a majority. A division vote based on actual voting is the usual practice and the Opposition members had demanded the same. Instead, the presiding officer just declared the Bill passed by voice vote without any division!
- Problem with process: A similar process was followed to pass the controversial farm laws (by the Rajya Sabha) in September 2020. The government seemed to lack a majority to pass the bills in the Upper House, and instead of a division vote, a voice vote was deemed to be adequate by the Deputy Speaker of the House. In both these cases, the disturbance caused in the House by the Opposition was used as a pretext to resort to a voice vote.
- Given the controversy around the farm laws, the government has repeatedly invoked multiple consultations around these laws.But finally, legislations were passed without an actual legislative majority voting has not been given due attention. And both were first passed as ordinances!
- Once they were tabled in the legislature, the governments insisted on the Bills not being referred to the legislative committees in either case.
- This was despite the fact that the Opposition repeatedly raised the demand.
- Money Bill route: The voice vote method supplements the other technique repeatedly deployed over the last few years to bypass the Upper House of the Parliament. It is the Money Bill route, which is increasingly used in instances even where the laws concerned would not easily fit within that definition. Most notoriously, the Aadhaar Bill was passed in this manner, a matter that then went to the Supreme Court.
- Other examples: The other controversial laws passed in the same manner include - (i) laws pertaining to electoral bonds, (ii) retrospective validation of foreign political contributions, (iii) the overhaul of the legal regime relating to tribunals, etc.
- Clear signal: The increasing use of the Money Bill route was defended by the Leader of the Rajya Sabha, who condemned the repeated questioning by the indirectly elected Rajya Sabha of the wisdom of the directly elected Lok Sabha. Underlying this common sentiment is a tendency to devalue bicameralism itself. The Lok Sabha is seen as directly representing the will of the people, and the Rajya Sabha as standing in its way. Democracy itself is seen purely in terms of parliamentary majority in the Lower House. So, the countervailing function of the Upper House is now rarely seen as legitimate.
- Rajya Sabha's significance: It has historically stopped the ruling party from carrying out even more significant legal changes. The notorious Emergency-era 42nd Constitutional Amendment could not be repealed in toto by the post-Emergency Janata regime. This is essentially because the Congress continued to have a strong presence in the Rajya Sabha. The Rajiv Gandhi government’s proposed 64th Constitutional Amendment Bill on Panchayati Raj was narrowly defeated in the Rajya Sabha. This was even though it enjoyed the highest ever majority in Lok Sabha.
- Bicameralism crucial for India: The two Houses are chosen by different processes of representation and elected on a different schedule. The very questioning of the monopoly of the Lower House to represent the ‘people’ makes bicameralism desirable. In India, the Rajya Sabha membership is determined by elections to State Assemblies. This leads to a different principle of representation, often allowing different factors to prevail than those in the Lok Sabha elections. The second chamber’s performance of a review role becomes particularly important. Bicameralism is especially significant in a Westminster system like India, where the Lower House is dominated by the executive.
- [message]
- 6. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (Prelims, Various GS Papers)
DRDO successfully launches VL-SRSAM
- A new missile: The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) conducted two successful launches of vertical launch short range surface-to-air missile (VL-SRSAM) off the Odisha coast in Balasore. The launches were carried out from a static vertical launcher from Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
- Details: Indigenously designed and developed by DRDO for the Navy, the VL-SRSAM is meant for neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges, including sea-skimming targets. The launches were carried out for demonstration of vertical launch capability as part of its maiden launch campaign. The missiles intercepted the simulated targets with pinpoint accuracy. They were tested for minimum and maximum range. The VL-SRSAM with weapon control system (WCS) was deployed during the trials.
- Supervised: The launches were monitored by senior scientists from various DRDO labs involved in the design and development such as DRDL, RCI, Hyderabad and R&D Engineers, Pune. The flight path and vehicle performance parameters were monitored using flight data, captured by various range instruments such as Radar, EOTS and telemetry systems deployed by the ITR, Chandipur. Trials have proved the effectiveness of the weapon system and few more trials will be conducted shortly before deployment on the ships. Once deployed, the VL-SRSAM system will prove to be a force multiplier for the Navy.
- DM: The Defence Minister Rajnath Singh congratulated DRDO on the successful trials. Dr. G Satheesh Reddy, Secretary, Department of Defence R&D and Chairman, DRDO congratulated the teams involved in the successful flight test of VL-SRSAM Missile System.
- Knowledge centre:
- ITR - The Integrated Test Range (ITR) is an Indian defence laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Located in Balasore, Odisha, it provide safe and reliable launch facilities for performance evaluation of rockets, missiles and air-borne weapon system.
- SAMs - A surface-to-air missile (SAM) is designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system. Missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons today, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first known idea for a guided surface-to-air missile was in 1925, when a beam riding system was proposed whereby a rocket would follow a searchlight beam onto a target. Missiles able to fly longer distances are generally heavier, and therefore less mobile. There are 3 classes of SAM systems; heavy long-range systems that are fixed or semi-mobile, medium-range vehicle-mounted systems that can fire on the move, and short-range man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS).
- Missile Guidance - SAM systems fall into two broad groups - those using radar and those using some other means. Longer range missiles generally use radar for early detection and guidance. Smaller missiles like MANPADS use infrared homing guidance systems. They are "fire-and-forget", and once launched they will home on the target on their own with no external signals needed.
- [message]
- 7. SOCIAL ISSUES (Prelims, GS Paper 2)
Pagri Sambhal Diwas - remembering the 1907 anti farm laws movement
- Feb 23 celebrated: As part of the ongoing farmers’ protest, the Samyukta Kisan Morcha (SKM) celebrated February 23 as ‘Pagri Sambhal Diwas'. It asked supporters across the globe to wear a green pagri/dupatta and post their pictures on social media, with the hashtag ‘Go green for farmers’.
- Ajit Singh: The farmers honour the memory of Ajit Singh, uncle of freedom fighter Bhagat Singh and founder of the Pagri Sambhaal movement of 1907. The "Pagrhi Sambhaal Jatta" was a successful farm agitation that forced the British government to repeal three laws related to agriculture back in 1907. Bhagat Singh’s uncle Ajit Singh was the force behind this agitation, and he wanted to channel people’s anger over the farm laws to topple the colonial government.
- Land Rights threatened: The three farm-related acts at the centre of the storm in 1907 were the Punjab Land Alienation Act 1900, the Punjab Land Colonisation Act 1906 and the Doab Bari Act.
- These acts would reduce farmers from owners to contractors of land, and gave the British government the right to take back the allotted land if the farmer even touched a tree in his field without permission.
- Amid resentment against the laws, Bhagat Singh’s father Kishan Singh and uncle Ajit Singh, with their revolutionary friend Ghasita Ram, formed Bharat Mata Society, aiming to mobilise this unrest into a revolt against the British government.
- Working hard to prepare the ground for the agitation against the three laws, they organised meetings in Lahore, addressed mostly by Kishan Singh and Ghasita Ram. Activists were sent especially to Lyallpur district to explain the three laws and their fallout to the public.
- Agitation's name: Ajit Singh persuaded Congress leader Lala Lajpat Rai to come on the stage during a rally in Lyallpur in March 3, 1907 to protest against the laws. Initially, Lala ji was not willing to join the agitation due to his assumptions that the movement was not limited to the farm agitation, as Ajit Singh did want to use it to revolt against the British. But Lala finally came on the stage and spoke wonderfully. Then, Banke Dayal, Editor of Jhang Sayal, read the historic song ‘Pagrhi sambhaal oh Jatta’, which became the anthem of the agitation.
- Britishers scared: On sensing the popular resentment, the British made minor amendment in the laws. An article by Bhagat Singh, published in daily newspaper ‘Pipal’ in 1931 and written from jail, noted, “Just before the public rally at Lyallpur in March 1907 , Lala ji told Ajit Singh that the government had made some amendments in Colony act. Ajit Singh made it clear to Lala ji that the agenda of the meeting was not to inspire the public to stop paying agri-taxes.
- Violence: The agitation couldn’t remain non-violent. Ajit Singh was booked for sedition after his speech at a public meeting in Rawalpindi on April 21, 1921. Violence erupted soon afterwards. There were riots in Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Lahore, etc. British personnel were manhandled, mud was flung at them, offices and churches were burnt, telegraph poles and wires cut. Lord Kitchener got terrified since the peasantry was becoming rebellious, and military and police were unreliable. Britishers felt that increase in land revenue was not the cause of this unrest. It was with a view to finishing British rule in India that it was being used as a political stunt. The result was that all the three laws were cancelled.
- End of the laws: British government repealed the three controversial laws in May 1907. It was a big victory for the farmer organisations.
- [message]
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
Indian activist gets Anti-corruption Champions Award
- What it is: An Indian social activist, Anjali Bhardwaj, who works on issues of transparency and accountability, has been selected for the “United State International Anti-Corruption Champions Award” along with the other 11 anti-corruption champions. These names were announced by Joe Biden administration.
- Key points: The Biden administration is of the view that these issues can be tackled only by working in coordination with the committed partners. These partners could be courageous individuals, who champion the anti-corruption efforts, and countries, which are working to fulfil their commitments with respect to the international anti-corruption standards.
- Anjali Bhardwaj: She is a 48-year-old activist who is also the founder of ‘Satark Nagrik Sangathan (SNS)’, a citizens’ group that promotes transparency and accountability in government and also encourage the active participation of citizens. She is a convener of National Campaign for People’s’ Right to Information. This campaign resulted into establishment of an anti-corruption ombudsman and Whistleblowers’ Protection Act.
- Other names: Other Champions include- Diana Salazar of Ecuador, Sophia Pretrick of Micronesia, Ardian Dvorani of Albania, Francis Ben Kaifala of Sierra Leone, Ibrahima Kalil Gueye of Guinea, Dhuha A Mohammed of Iraq, Juan Francisco Sandoval Alfaro of Guatemala, Mustafa Abdullah Sanalla of Libya, Bolot Temirov of Kyrgyz Republic, Victor Sotto of The Philippines and Ruslan Ryaboshapka of Ukraine.
- Whistleblower Protection Act, 2014: A whistleblower is an insider who exposes some fraud to the world. The said Act comprises provisions to receive the complaints related to corruption or wilful misuse of power or discretion against any public servant. It also provides for the mechanism to inquire or cause inquiry into such complaints.
- Which policy: The National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) has published its draft national policy on migrant labours. It was prepared in association with the working subgroup of officials and members of civil society. It is inspired by the rights-based approach which gain momentum during the return migration of around 10 million migrant workers from cities to their respective village during the Covid-19 pandemic and lockdown.
- Facts: The draft migrant workers policy describes two approaches regarding the policy design. The first approach focusses on cash transfers, special quotas, and reservations for the labours. The other approach seeks to enhance the agency and capability of community. Thus, in turn removes any of the aspects coming in the way of natural ability of the individual to prosper. Policy also seeks to remove the restrictions on true agency and potential of the migrant workers. It was formulated with the goal of “not providing any temporary or permanent economic aids as well as the social aids”.
- Internal migration: The policy further maintains that, “Internal Migration should be considered as an integral part of the development and government’s policies should be formulated in such a way that it facilitates the migration”.
- Need: This draft policy was formulated in the light of flaws in the existing laws. A report of 2017 also stated that the migrant workers should be integrated with all other workers so as to overarch the exploitation of workers by contractors. Further, in India the size of the unorganised sector is huge so a comprehensive policy was required to provide them a social protection.
- Ending suicide: Japan has appointed the first ever Minister for Loneliness amid the increasing suicide rates in Japan. Suicide rates in Japan has increased for the first time in 11 years in the current COVID-19 pandemic situation.
- Tetsushi Sakamoto to the rescue: Japan appointed the loneliness minister on the lines of US, which became the first country in world to create a similar position in the country in 2018. Tetsushi Sakamoto, who is in charge of combating Japan’s falling birth rate and revitalising regional economies, was also appointed as the Loneliness minister. The government created an “isolation or loneliness countermeasures office on February 19, 2021 within its cabinet. This office will look after the issues like suicide and child poverty which have increased amid the ongoing pandemic.
- Suicides in Japan: Death by suicide is considered a major social issue in Japan. In the year 2017, the country had witnessed seventh highest suicide rate in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The suicide rates had increased by 34.7% during the 1997 Asian financial crisis. The rates were at peak in 2003 after that, the rates have been decreasing. The rates were at its lowest in the year 2019. However, the monthly suicide rates in Japan increased by 16% in between July and October 2020 because of COVID-19. Among the total cases, seventy percent of suicides are male. Suicide has become the leading cause of death for man in the age group of 2- years to 44 years.
- What it is: The Central government has launched the ‘National Urban Digital Mission’ on February 23, 2021. It was launched by the Union Housing & Urban Affairs Minister, Hardeep Singh Puri and Minister of Electronics & IT, Ravi Shankar Prasad.
- Goals: The mission will institutionalise the citizen-centric and ecosystem-driven approach for the urban governance and service delivery in cities by the year 2022. It will also be providing these service deliveries in all cities and towns by 2024. Initiatives like Smart-Code, India Urban Data Exchange (IUDX), Smart Cities 2.0 website, and Geospatial Management Information System (GMIS) were also launched at this virtual event. The "India Urban Data Exchange (IUDX)" initiative was developed by the Smart Cities Mission in partnership with the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
- National Urban Digital Mission: This mission was launched in order to create a digital infrastructure for all the cities in country. It will help in creating a shared digital infrastructure which in turn can be used to consolidate and cross-leverage the several digital initiatives of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- India Urban Data Exchange (IUDX): It is an open-source software platform facilitating a secure and authenticated exchange of data across several data platforms, data producers, 3rd party applications and consumers. IUDX will provide full control to the data owners regarding the sharing of data. They could control as to what data needs to be exposed and to whom.
9.1 Today's best editorials to read
- We offer you 7 excellent editorials from across 10 newspapers we have scanned.
- [message]
- SECTION 3 - MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)