Useful compilation of Civil Services oriented - Daily Current Affairs - Civil Services - 10-02-2021
- People and Personalities - Nigerian economist Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala as WTO chief - The World Trade Organization (WTO) announced that Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala (Nigeria) was “best poised to attain consensus” to become its seventh Director-General. This Nigerian economist will hence be the new Chief of World Trade Organisation (WTO). The former Finance Minister of Nigeria will become the first woman and African to take up this position. The development comes after the administration of US President Joe Biden showed its support for the same on February 5, 2021. Roberto Azevêdo had stepped down as WTO Director-General on 31 August 2020, a year before the expiry of his mandate. The incoming chief of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) has a reputation for shaking up the guardians of wealth and power that will come in handy in her new role.
- Healthcare and Medicine - Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine in India - The NITI Aayog member (health and nutrition) Vinod Kumar Paul said that US giant Johnson & Johnson was interested in manufacturing its COVID-19 vaccine in India. The Janssen vaccine is produced by Janssen Biotech, the pharmaceutical arm of Johnson & Johnson. By Feb 2021, India ha approved AstraZeneca's Covishield vaccine and Bharat Biotech's Covaxin for emergency use. Unlike the Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, which are based on a new technology called mRNA that uses the body's own cells to produce a key viral protein, the J&J vaccine uses a type of virus called an adenovirus to deliver genes that produce those same viral proteins.
- Science and Technology - NASA's SPHEREx mission to be launched by SpaceX - The NASA's SPHEREx mission, that SpaceX will launch, will be used by astronomers to gather data on over 300 million galaxies, as well as over 100 million stars in Milky Way. The Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer mission (SPHEREx) will provide the first all-sky spectral survey. The launch date is Jun 17, 2024. Every six months, SPHEREx will survey the entire sky using technologies adapted from Earth satellites and interplanetary spacecraft. The mission will create a map of the entire sky in 96 different color bands, far exceeding the color resolution of previous all-sky maps. It also will identify targets for more detailed study by future missions, such as NASA's James Webb Space Telescope and Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope. The mission will search for water and organic molecules in stellar nurseries.
- Social Issues - China faces fertility crisis - The number of newborns in China dropped by 15% in 2020 as compared to 2019, according to the Ministry of Public Security. In 2020, China had reported 1,00,35,000 births, while the country had registered 1,17,90,000 births in 2019. The decline came amid the coronavirus pandemic and the economic uncertainties associated with it. Demographers called on China to immediately abandon restrictions on having babies, be more tolerant toward babies born out of wedlock, and do more to lower the costs of raising and educating children. The birth rate on the Chinese mainland dropped to 10.48 per 1,000 people in 2020, the lowest in seven decades, and the number of births was down 580,000 compared with the previous year. The total fertility rate (the average number of children a woman gives birth to) should remain at about 2.1 for China's population to stay stable, and a total fertility rate of 1.5 is a highly sensitive warning line.
- Energy - India to make up biggest share of energy demand growth by 2040, says IEA - The International Energy Agency (IEA) said India will make up the biggest share of energy demand growth at 25% over the next two decades. IEA expects India's oil demand to rise to 8.7 million bpd in 2040 from 5 million bpd in 2019. Rising oil demand could take India's import bill to $255 billion by 2040. For now, coal, oil, and natural gas were the three primary commercial energy sources. India's energy policy, till the end of the 1980s, was mainly based on availability of indigenous resources. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is the nodal Ministry of the Government of India for all matters relating to new and renewable energy.
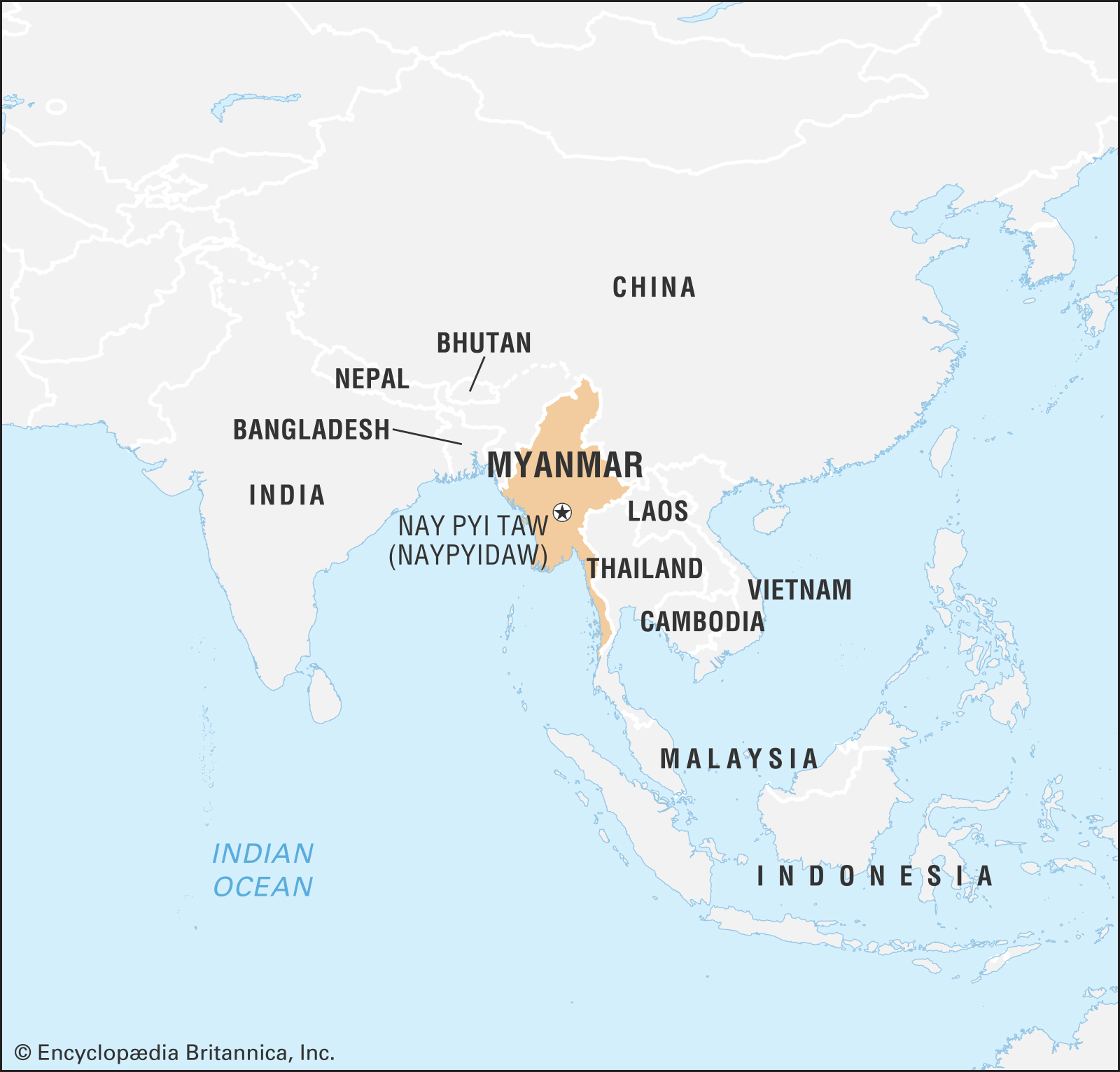
- World Politics - Myanmar police battle protesters defying ban - Myanmar Police fired rubber bullets and used teargas against protesters defying a ban on large gatherings in the capital, Naypyidaw. Water cannons were also used at demonstrators opposing the military coup and demanding the release of leader Aung San Suu Kyi and others. Myanmar's military Tatmadaw has seized full control of the country's government and detained civilian leader Aung San Suu Kyi along with hundreds of members of her National League for Democracy (NLD) party in a move the Biden administration has labeled a “coup.”
- World Economy - Bitcoin crosses $47,000 after Tesla's $1.5 billion purchase - Bitcoin on 09-02-2021 hit a fresh record of more than $47,000 after Elon Musk-led Tesla announced that it has invested $1.5 billion, or 8% of its reserves, in the largest cryptocurrency. The company said it would soon accept bitcoin as a form of payment for its electric cars. Bitcoin is up around 1,000% since March 2020. Cryptocurrencies, especially Bitcoin, is now being considered as a safe-haven asset against market volatility and inflation. The current societal and economic climate also brings about a situation for people to hold less cash and stay hedged against market swings.
- World Politics - New Zealand suspends ties with Myanmar - New Zealand's PM Jacinda Ardern on February 9, 2021 announced the suspension of ties with Myanmar. Ardern said that the government will suspend all high-level political and military contact with Myanmar. It will also impose a travel ban on the military leaders of Myanmar and ensure its aid programme to the country will not include projects that benefit the military government. New Zealand's Foreign Minister Nanaia Mahuta said in a separate statement that New Zealand does not recognise the legitimacy of the military-led government and called on the military to immediately release all detained political leaders and restore civilian rule.
- Energy - South Korea to build world’s largest offshore wind farm - SK will build the world's largest offshore wind farm by 2030. This 8.2GW offshore wind power complex will come up in Jeonnam province. The announcement was made on February 5, 2021 by the Moon Jae-In administration after signing a USD 43 billion deal. South Korea seeks to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. Carbon neutrality means having a balance between emitting carbon and absorbing carbon from the atmosphere in carbon sinks. It is essential to reduce carbon emissions in order to reach climate neutrality. A net-zero emissions balance is achieved when the amount of greenhouse gas released into the atmosphere is neutralised.
- Governance and Institutions - Government to invest Rs. 400 crores in Goa for fisheries hub - The Union Fisheries Minister Giriraj Singh on February 7, 2021, announced an investment of Rs.400 crores in Goa for making the coastal state a fisheries hub in India. Goa has the potential for the highest fish production in India and it has the capacity to become a fisheries hub. The investment will be jointly raised by the central government, state fisheries board, and others. India is the second largest producer of fish in the world contributing to 5.43% of global fish production. The sector provides livelihoods to about 16 million fishers and fish farmers at the primary level and almost twice the number along the value chain. Fish being an affordable and rich source of animal protein, is one of the healthiest options to mitigate hunger and malnutrition. In India, the Primary sector comprises agriculture, forestry, fishing and mining & quarrying activities; Secondary sector comprises manufacturing, electricity, gas, water supply & other utility services and construction, and Tertiary sector comprises all services. The fishing and aquaculture sector had a GVA of Rs.2.22 lakh crores in 2019-20.
- [message]
- SECTION 2 - DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- [message]
- 1. ECONOMY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Spending to push GDP growth
- Recession and Budget spending: India faced a huge recession in 2020, with the economy shrinking rapidly. Budget 2021-22 tries to give an expenditure push to the economy. Questions arise about its efficacy and timely impact. A key issue is fiscal position of states, hit due to Covid lockdowns, and GST shortfalls.
- Immediate future: The Finance Ministry has said that expenditure increase in January-March quarter of FY21 and in April-June quarter of FY22 will start showing results from the beginning of the next fiscal (April-May 2021). Centre has sanctioned ?11,800 crore as part of the special interest-free 50-year loans and nearly half of them have already been disbursed. Centre expects there will not be lag in expenditure and its impact and the process will continue with the expenditure flow.
- Atmanirbhar bano: Under Atmanirbhar Bharat, the Centre announced that it will give Rs. 12,000 crore under special interest-free 50-year loans for capital expenditure. Nearly ?6,000 crore has been disbursed to States under special interest-free 50-year loans. The remaining amount is likely to be disbursed before March-end. For the fiscal year 2020-21, the government increased the total expenditure to Rs. 34.5 lakh crore in the Revised Estimate (RE) from Rs. 30.42 lakh crore of Budget Estimate (BE).
- Revenue expenditure: If revenue expenditure has gone up (from ?26.33 lakh crore to Rs. 30.11 lakh crore), so has the Capital Expenditure (from Rs. 4.12 lakh crore to over Rs. 4.39 lakh crore). For the current fiscal, out of total expenditure of Rs. 34.83 lakh crore, revenue share is nearly Rs. 29.2 lakh crore, while capital share is Rs. 5.54 lakh crore. Increase in expenditure was during November-December period. Reverting to provision of spending 33 per cent of BE in the last quarter and 15 per cent of BE in March, as against 25 per cent and 10 per cent respectively, also aims to increase the expenditure to give boost to economic recovery.
- CGA data: Data from the Controller General of Accounts (CGA) show that total expenditure during April- December period was nearly 75 per cent of BE, which was similar to the corresponding period of FY2019-20. This is significant, considering heavy checks on expenditure during the first seven months of the current fiscal. The pace of expenditure during the remaining period of the fiscal has increased not just for the Centre but also for the States. Now, the pace will continue during the first quarter of the next fiscal, which is basically front loading of expenditure.
- Front-loading: The government is front loading its expenditure in the first quarter to get maximum advantage of government expenditure on the economy in that particular year. During FY17-FY20, the Union Government expenditure in the first quarter has been more than 25 per cent, confirming to front loading theory. Even in this fiscal, the first quarter expenditure (Rs. 81,59,440 crore) is higher than expenditure in second (Rs. 66,34,660 crore) and third quarter (Rs. 80,07,370 crore). While the first round impact of government expenditure on GDP will be realised in the quarter expenditure is done, second round impact in the form of PFCE (Private Final Consumption Expenditure) may be felt with a lag.
- Summary: The Indian economy needs a big spending push from the government. However, the Budget 2021-22 remained focused on Supply side and not on Demand side. And the revenue-constrained government is trying hard to have the multiplier effect of infrastructure spending to kick in. Time will tell if the measures worked out or not. For the economy, a sustained real GDP growth rate of 8% is crucial, if demographic dividend is to be realised over the decade.
- [message]
- 2. ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper
Story of Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary
- Guests arrive: More than a lakh migratory water birds arrived at the Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary in Himachal Pradesh in winter 2020-21. It is located in the Kangra District of Himachal Pradesh.
- History: In 1975, Pong dam was built across the Beas River. It is also called the Pong reservoir or the Maharana Pratap Sagar. In 1983, the entire reservoir was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary by the Himachal Pradesh government. In 1994, the Government declared it a “Wetland of National Importance”, and in 2002, the Pong Dam Lake was declared as Ramsar Site.
- Destination for migratory birds: The sanctuary plays host to around 220 species of birds belonging to 54 families. Migratory birds from all over Hindukush Himalayas and also as far as Siberia come here during winter.
- Rivers: The lake is fed by Beas River and its numerous perennial tributaries such as Gaj, Neogal, Binwa, Uhl, Bangana, and Baner. It harbours around 22 species of fish, including rare fish like sal and gad. The adequate water level of the lake makes it an ideal destination to indulge in water sports.
- Vegetation: The sanctuary area is covered with tropical and subtropical forests, which shelters a great number of Indian Wildlife animals. Flora includes eucalyptus, acacia, jamun, shisham, mango, mulberry, ficus, kachnar, amla and prunus. Fauna includes barking deer, sambar, wild boars, nilgai, leopards and oriental small-clawed otters. Avian-Fauna includes black-headed gulls, Red necked grebes, plovers, terns, ducks, water-fowl egrets, and more.
- National Parks in Himachal Pradesh:
- Great Himalayan National Park: This park, located in the Banjaar sub-division of Kullu district, was officially declared as a National Park in 1999. In 2014, the Great Himalayan National Park received the status of being a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its wonderful contribution towards biodiversity conservation. The species found here are Greater Blue Sheep, Indian Pika, Rhesus monkey, Himalayan black bear, Himalayan brown bear, Red fox, Mongoose.
- Pin Valley National Park: This park, located in Lahaul and Spiti District, was established in 1987. Various endangered species including the snow leopard and Siberian ibex find their natural habitat.
- Inderkilla National Park: This is located in the Kullu district in Himachal Pradesh and established in 2010. Animals of the Himalayan region like leopards, deers and, birds which even include the rare birds of the summer season, and insect species are varied and can be seen from time to time.
- Khirganga National Park: This park is located in Kullu and was established in 2010. The national park is situated at a height of around 5,500 meters and is spread across an area of about 710 square kilometers.
- Simbalbara National Park: This is located in the Paonta Valley of Sirmour District. The national park was established in 1958 as the Simbalbara Wildlife Sanctuary covering an area of 19.03 square kilometers. In 2010, it was turned into a national park by merging an additional 8.88 square kilometers of the area to its boundaries.
- Massive air pollution: News of lakhs of deaths due to air pollution disturbs citizenry. Action is warranted.
- Steps taken: More than 250 continuous & 800 ambient air quality monitoring stations are operating across the country. Budget allocation for air pollution was increased significantly in 2020-21 to ensure cleaner air in million plus cities. The Commission for Air Quality Management was established which penalises the polluters in the NCR. India has jumped from BSIV to BSVI vehicles & now the focus is shifted towards e-mobility. The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana has increased the LPG coverage in rural areas which has reduced indoor air pollution.
- innovations: Many institutions are involved in the process of developing solutions to combat the air pollution. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) has developed PUSA Bio Decomposer which converts crop residue into manure in 15-20 days, a cost-effective alternative to tackle stubble burning. UNDP promotes start-up led innovations like filter-less retrofit device to cut down the particulate matter at source level. Breathing root technology is developed to improve indoor air quality by purifying the air. The UNDP & the University of Nottingham has developed GeoAI platform to identify non-complaint brick kilns. The platform has mapped over 37,000 brick manufacturing units across the Indo-Gangetic plains.
- Road ahea: Government needs to support the enterprises to come up with scalable pollution abatement technologies. A single window online platform needs to be developed to showcase innovations to mitigate air pollution. Private sector needs to innovate their operations, functioning & build emission and pollution controls to reduce carbon footprint.
- [message]
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
- 3. FOREIGN AFFAIRS (Prelims, GS Paper 3, Essay paper)
Treading gently - India-Myanmar relations
- End of all tensions: The long-lingering power struggle in Myanmar ended as the Myanmar junta (military) toppled the democratically elected government in a coup. This smashed decade-long hopes for a truly democratic Myanmar. For all nations in the region, especially China and India, there are major implications.
- Why Myanmar: India and Myanmar relationship started after the Treaty of Friendship was signed in 1951. The foundation for a more meaningful relationship was established during Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi’s visit in 1987. Both have traditionally had much in common, with cultural, historical, ethnic, and religious ties, in addition to sharing a long geographical land border and maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal. Myanmar is geopolitically significant to India as it stands at the center of the India-Southeast Asia geography. It is the only Southeast Asian country that shares a land border with northeastern India, stretching some 1,624 kilometers. The two also share a 725-km maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal.
- Doctrines: Myanmar is the only country that sits at the intersection of India’s “Neighborhood First” policy and its “Act East” policy. It is an essential element in India’s practice of regional diplomacy in the Indo-Pacific and serves as a land bridge to connect South Asia and Southeast Asia. For India to become an assertive regional player in Asia, it has to work toward developing policies that would improve and strengthen its relationship with neighboring countries. In pursuance of this, China is a big roadblock, as it aims to diminish India’s influence in its neighborhood. Therefore, both India and China are fighting for gaining influence in Myanmar.
- SAGAR: As part of its policy for the Indian Ocean called Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), India developed the Sittwe port in Myanmar’s Rakhine state. The Sittwe port is meant to be India’s answer to the Chinese-fronted Kyaukpyu port, which is intended to cement China’s geostrategic footprint in Rakhine.
- Insurgencies: The north-eastern states in India are affected by left-wing extremism and narcotics trade routes (golden triangle). To counter these threats, the Indian and Myanmar armies have carried out many joint military operations like Operation Sunshine.
- Commerce: Many Indian companies made significant economic and trade agreements in infrastructure and other areas. Some other Indian companies such as Essar, GAIL, and ONGC Videsh Ltd. have invested in Myanmar’s energy sector. To elevate its “Made in India” arms industry, India has identified Myanmar as key to increasing its military exports.
- Implications: The coup has attracted strong reactions and the threat of sanctions from the United States and the West, and can lead to some new political realignments in Myanmar. Decisive western sanctions may force Myanmar’s military to get closer to China, which may not be in the interest of India. A failed Myanmar state at India’s doorstep and a weakened Myanmar falling into the clutches of China as a satellite state may increase China’s bidding in regional affairs. Any effort to restore democracy in Myanmar will require supporting Aung San Suu Kyi. However, due to her silence on the Rohingya crisis, the plight of the hapless Rohingya may take a backseat or be conveniently forgotten. This is not in India’s national security interest in the north-east.
- Summary: Myanmar’s importance to India’s conduct of cultural diplomacy through the lens of Buddhism for tourism purposes. India’s “Buddhist Circuit” initiative, which seeks to double foreign tourist arrivals and revenue by connecting ancient Buddhist heritage sites across different states in India, should resonate with Buddhist-majority Myanmar. This can build up India’s diplomatic reservoir of goodwill and trust with Buddhist-majority countries such as Myanmar. Infrastructure projects such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport (KMMTT) should be financed into fruition expeditiously. And, the quicker the Rohingya issue is resolved, the easier it will be for India to manage its relations with Myanmar and Bangladesh, focusing instead more on bilateral and subregional economic cooperation.
- [message]
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
- 4. GOVERNMENT SCHEMES (Prelims, GS Paper 2, Essay paper)
Street Vendors get government support
- Helping those who need it: The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) will launch the ‘Main Bhi Digital (me too digital)’ drive for the street vendors to enable them to accept and make payments digitally. The drive was encouraged by the success of the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PMSVANidhi) scheme, launched in the wake of the Covid-19 lockdown, to provide vendors microcredit.
- Highlights:
- Main Bhi Digital Drive - As part of the new drive, between 4th January to 22nd January 2021, over 10 lakh street vendors across the country who have availed of the Rs. 10,000 loan will be trained in using digital payments. The vendors would be able to not just receive payments digitally but also pay for material they procure from sellers using unique QR codes. The mobile phones of the vendors will be equipped with the software needed for the transactions, and training provided to them on safe and secure payments.
- PM SVANidhi Scheme - It is a scheme of the MoHUA launched in June 2020 which entitles the street vendors to Rs. 10,000 interest-free loan as working capital to restart their businesses. Data shows that only 20% of the beneficiaries are digitally enabled.
- Street Vendors in India: Anyone who doesn’t have a permanent shop is considered a street vendor. According to estimates, street-vending accounts for 14% of the total (non-agricultural) urban informal employment in the country. There are an estimated 50-60 lakh street vendors in India, with the largest concentrations in the cities of Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Ahmedabad.
- Issues: Licence caps are unrealistic in most cities, for example, Mumbai has a ceiling of around 15,000 licences as against an estimated 2.5 lakh vendors. So most vendors hawk their goods illegally, which makes them vulnerable to exploitation and extortion by local police and municipal authorities. Often, local bodies conduct eviction drives to clear the pavements of encroachers, and confiscate their goods. Fines for recovery are heavy.
- Organizations:
- National Association of Street Vendors of India (NASVI): It is a membership based organization of 1,024 street vendors organizations representing 10,00,000 street vendors from almost all parts of India.
- National Hawker Federation (NHF): It is an association of street vendors across 28 States in the country, with 1,188 Unions, including 11 Central Trade Unions and over 20 International Trade Unions abroad.
- Other initiatives: The Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014 was enacted to regulate street vendors in public areas and protect their rights. The Act defines a “street vendor” as a person engaged in vending of articles of everyday use or offering services to the general public, in any public place or private area, from a temporary built up structure or by moving from place to place”.
- Socio-economic: The government has also launched its first-ever official socio-economic survey of vendors, to bring street vendors under schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana, the Jan-Dhan Yojana, Building and Other Construction Workers Act 1996, the Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana, the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana etc.
- Summary: Despite multiple schemes running for the street vendors, there are various gaps in implementation, identification, awareness and accessibility of various schemes which should be plugged in a timely manner. Benefits like maternity allowances, accident relief, natural death compensation, education support for children for higher studies, pension during any crisis should be provided to them.
- [message]
- 5. POLITY AND CONSTITUTION (Prelims, GS Paper 2, GS Paper 3)
Uniform Civil Code (UCC)
- Constitutional background: The Article 44 of the Indian Constitution states that “the State shall endeavour to secure for the citizens a uniform civil code (UCC) throughout the territory of India.” The desirability of a uniform civil code is consistent with human rights and the principles of equality, fairness and justice. The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) calls for the formulation of one law for India, which would be applicable to all religious communities in matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, adoption. However, many practical challenges exist, making its desirability suspect.
- Background of Uniform Civil Code: The origin of the UCC dates back to colonial India when the British government submitted its report in 1835 stressing the need for uniformity in the codification of Indian law relating to crimes, evidence, and contracts, specifically recommending that personal laws of Hindus and Muslims be kept outside such codification. Increase in no. of legislations dealing with personal issues in the far end of the British rule forced the government to form the B N Rau Committee to codify Hindu law in 1941.
- Personal laws: Based on these recommendations, a bill was then adopted in 1956 as the Hindu Succession Act to amend and codify the law relating to intestate or unwilled succession, among Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, and Sikhs. However, there were separate personal laws for Muslims, Christians and Parsis. In order to bring uniformity, the courts have often said in their judgements that the government should move towards a uniform civil code. The judgement in the Shah Bano case is a well known one.
- Centre's stand: By arguing that practices such as triple talaq and polygamy impact adversely on the right of women to a life of dignity, the Centre has raised the question whether constitutional protection given to religious practices should extend even to those that are not in compliance with fundamental rights.
- UCC and implications: Supporters of UCC claim that -
- Protection to vulnerable sections of society: The UCC aims to provide protection to vulnerable sections as envisaged by Ambedkar including women and religious minorities, while also promoting nationalistic fervour through unity.
- Simplification of laws: The code will simplify many complex laws around marriage ceremonies, inheritance, succession, adoptions making them one for all. The same civil law will then be applicable to all citizens irrespective of their faith. When enacted, the code will work to simplify laws that are segregated at present on the basis of religious beliefs like the Hindu code bill, Sharia law, and others.
- Adhering to secularism: Secularism is the key objective enshrined in the Preamble, and a secular republic needs a common law for all citizens rather than differentiated rules based on religious practices.
- Gender justice: India has separate sets of personal laws for each religion governing marriages, divorce, succession, adoption and maintenance. However, the rights of women are usually limited under religious law, be it Hindu or Muslim. The practice of triple talaq is a classic example. If a uniform civil code is enacted, all personal laws will cease to exist. It will do away with gender biases in Muslim law, Hindu law and Christian law that have been often challenged by women on the ground that they violate the right to equality.
- Challenges to UCC: Opponents say that -
- Exceptions in central Family Laws: The preliminary sections in all central family law Acts enacted by Parliament since independence declare that they will apply to “the whole of India except the state of Jammu and Kashmir.” A second exception was added in 1968 in all these Acts, pronouncing that “nothing herein contained shall apply to the Union Territory of Pondicherry.” A third exception, none of these Acts applies in Goa, Daman and Diu. A fourth exception, relating to the north-eastern states of Nagaland and Mizoram, emanates from Articles 371A and 371G of the Constitution, decreeing that no parliamentary legislation will replace the customary law and religion-based system for its administration.
- Communal politics: The demand for a uniform civil code has been framed in the context of communal politics. A large section of society sees it as majoritarianism under the garb of social reform. That takes away its moral standing completely. A law enforced with such colour is not one accepted by heart.
- Constitutional hurdle: Article 25 of Indian constitution, that seeks to preserve the freedom to practise and propagate any religion, gets into conflict with the concepts of equality enshrined under Article 14.
- Road ahead: The government and society will have to work hard to build trust, but more importantly, make common cause with social reformers rather than religious conservatives. Rather than an omnibus approach, the government could bring separate aspects such as marriage, adoption, succession and maintenance into a uniform civil code in stages. The government would also do well to complement the overdue move towards a uniform civil code with a comprehensive review of several other laws in the context of gender justice. Bringing Jammu and Kashmir into the country’s mainstream of family laws is an exercise that needs to be undertaken also for Goa, Daman and Diu, Puducherry, Nagaland and Mizoram. The citizens’ fundamental rights to equality before law and equal protection of the laws guaranteed by the Constitution call for a similar action in respect of these territories as well. So does the provision of Article 44 enjoining the state to make endeavours to secure for the citizens a uniform civil code throughout the territory of India.
- [message]
- 6. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (Prelims, Various GS Papers)
Magic of 5G technology
- 2021 move: The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) sought inputs from telecom companies and other industry experts on the sale and use of radio frequency spectrum over the next 10 years, including the 5G (Fifth Generation) bands. The world over, implementation of 5G has slowly commenced. But the government is not auctioning any spectrum for 5G for now, instead releasing more in 4G range.
- Features of 5G technology: This will not just be about higher speeds, but about enablement of a whole new system of services that are unimaginable today.
- Millimeter wave spectrum: The 5G networks will operate in the millimeter wave spectrum (30-300 GHz) which have the advantage of sending large amounts of data at very high speeds because the frequency is so high, it experiences little interference from surrounding signals.
- Upgraded LTE: 5G is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks
- Internet speed: In the high-band spectrum of 5G, internet speeds have been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (gigabits per second) as compared to the maximum internet data speed in 4G recorded at 1 Gbps. 5G network speeds should have a peak data rate of 20 Gb/s for the downlink and 10 Gb/s for the uplink.
- Bands in 5G: 5G mainly work in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high frequency spectrum — all of which have their own uses as well as limitations.
- Low band spectrum: It has shown great promise in terms of coverage and speed of internet and data exchange however the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- Mid-band spectrum: It offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- High-band spectrum: It has the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
- Problems: The road is not easy at all!
- Enabling critical infrastructures: 5G will require a fundamental change to the core architecture of the communication system. The major flaw of data transfer using 5G is that it can't carry data over longer distances. Hence, even 5G technology needs to be augmented to enable infrastructure.
- Financial liability on consumers: For transition from 4G to 5G technology, one has to upgrade to the latest cellular technology, thereby creating financial liability on consumers.
- Capital inadequacy: Lack of flow of cash and adequate capital with the suitable telecom companies (like Bharti Airtel and Vodafone Idea) is delaying the 5G spectrum allocation.
- Utility of 5G Applications: Combined with IoT, cloud, big data, AI, and edge computing, 5G could be a critical enabler of the fourth industrial revolution. To make it succeed, really benefical applications need to be imagined. 5G networks could improve the accessibility of services such as mobile banking and healthcare, and enable exponential growth in opportunities for unemployed or underemployed people to engage in fulfilling and productive work. For this Government has rolled out enabling policies.
- Enabling policy: India’s National Digital Communications Policy 2018 highlights the importance of 5G when it states that the convergence of a cluster of revolutionary technologies including 5G, the cloud, Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, along with a growing start-up community, promise to accelerate and deepen its digital engagement, opening up a new horizon of opportunities. It aims to reach 100% teledensity, high-speed internet highways and delivery of citizen-centric services electronically.
- Global progress on 5G: Telecom companies have already started building 5G networks and rolling it out to their customers in many countries: 5G had been deployed in 50 cities in the United States, and South Korea has rolled out 5G to 85 cities. Japan and China have too started 5G mobile service on a trial basis.
- China angle: One of the foremost leaders in 5G technology is China, where firms like Huawei offer best telecom gear at low prices. Ex-President Trump had banned such firms, as part of the trade war. India too has had serious reservations with Chinese firms, after the 2020 LAC problems. Hence, newer solutions are being found and implemented, like what the Reliance JIO is planning with indigenous components.
- [message]
- 7. SOCIAL ISSUES (Prelims, GS Paper 2)
Digital education: Boon or Bane
- Pandemic hit hard: The Covid-19 outbreak disrupted children’s lives everywhere, pushed many out of formal schooling, and literally stalled classes and examinations across India. To ensure students do not miss out on studies, schools shifted the classes to online mode. But it's easier said than done.
- Upheaval: Many students were left clinging to their phones and computer screens, and many had no internet. The 2017-18 National Sample Survey suggested that less than 15% of rural Indian households have Internet as opposed to 42% of their urban counterparts. So the shift to the e-learning system has sparked a debate on whether it helped the students to learn or has impeded their progress, social and emotional well-being, and more importantly if this is indeed education.
- Digital education: It is the innovative use of digital tools and technologies during teaching and learning and is often referred to as Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) or e-Learning. Exploring the use of digital technologies gives educators the opportunity to design engaging learning opportunities in the courses they teach, and these can take the form of blended or fully online courses and programs.
- Government initiatives: Several initiatives have been taken to enable online education in India, such as (a) E-PG Pathshala: An initiative of the Ministry of Human Resource Development to provide e-content for studies, (b) SWAYAM: it provides for an integrated platform for online courses, (c) NEAT: It aims to use Artificial Intelligence to make learning more personalized and customized as per the requirements of the learner, (d) National Project on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL), National Knowledge Network, (NKN), and National Academic Depository (NAD), among others.
- Technology as a saviour: Online education enables both the teacher as well as the students to set their own learning pace plus provides the flexibility of setting a schedule that fits everyone’s agenda. Consequently, providing a better work-study balance. In a space as vast and wide as the internet, infinite skills and subjects are there to teach and learn. A growing number of universities and higher education schools are coming forward to offer online versions of their programs for various levels and disciplines. Lesser monetary investment is needed, with better results. With the online mode of learning, the money spent on study materials along with commute charges is considerably less. Online learning allows students to work in the environment that best suits them.
- Problems: Education is not just about classes but interactions, broadening of ideas, and free-flowing open discussions. Students learn more from each other while engaging in challenging collective tasks and thinking together. There is substantial learning that is lost when education goes online. Staring at a screen prevents them from using their mind and acting as remote receptors of what is beamed. Not everyone who can afford to go to school can afford to have phones, computers, or even a quality internet connection for attending classes online. Due to this, the mental stress that students have to undergo is very high.
- Contradictory to Right to Education (RTE): Technology is not affordable to all, shifting towards online education completely is like taking away the Right to Education of those who cannot access the technology. Moreover, the National Education Policy that talks about the digitization of education is also in contradiction with the right to education.
- Health issues: Younger students, especially in classes 1 to 3 were most likely to suffer from eye-health issues due to staring at the computer or mobile screen for extended periods. Other health issues like neck and back pain etc. due to bad posture and lack of movement have been noticed in older students.
- Road ahead: Flexible rescheduling the academic timetable and exploring options in collaboration with schools, teachers, and parents for providing access to education to a larger section of students. Staggering teacher-student interactions in physical mode with not more than 50% of the total strength attending schools on alternate days. Giving priority to the less advantaged students who do not have access to e-learning. Genuine efforts must be invested to ensure every child gets good quality equitable education as a fundamental right. Shorter but quality discussions rather than long hours of monotonous sitting and one-way communication, should be preferred. And finally, authorities must accept (and hence try to resolve) the problem that millions of students are left out of the mainstream of education due to the online shift.
- [message]
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
- 8. MISCELLANEOUS (Prelims, GS Paper 1, GS Paper 2)
United States to re-join UNHRC
- Back again: The Joe Biden administration in US is all set to re-join the UN Human Rights Council. The United States had withdrawn from the council in the year 2018 under Presidency of the Donald Trump.
- Story: President Trump withdrew from the world body’s main human rights because of its disproportionate focus on Israel. Israel had received the largest number of critical council resolutions so far with respect to any other country. So, the Trump administration discussed the issue with the body’s membership. The members include Cuba, China, Russia, Eritrea and Venezuela. All these countries have been accused of human rights abuses.
- About UN Human Rights Council (UNHCR): It is an inter-governmental body within the UN system, involved in strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights across the world. It looks after the situations of human rights violations and recommends on the situations, and was created in the year 2006 by the UN General Assembly Resolution 60/251. Its first session of the council took place in 2006 three months after its establishment, and it was created after replacing the United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR). The council comprises of the 47 UN Member States, elected by the UNGA by a direct and secret ballot.
- A new deal: India and Afghanistan have inked the deal to build a dam, called Sahtoot dam, in order to supply water to the Kabul City. Following the deal, the prime minister of India called for a ceasefire in Afghanistan in order to end a spike in violence.
- The story: PM Modi expressed his concern over increase in violence in Afghanistan, and the President of Afghanistan, Ashraf Ghani, also stated that both the countries want a terrorism free region. President Ghani sought guarantees for stability in Afghanistan.
- About the Dam: It is a proposed dam in the Kabul river basin, whose construction will provide drinking, irrigation and Environmental water in the Kabul province of Afghanistan. The dam will be completed at the cost of about US$120 to $305 million, and will be constructed by India. The design will be completed by an Iranian firm. The dam will provide waters to irrigate 4000 hectares of land in Charasiab and Khairabad districts of Kabul. The dam will also provide drinking water to a New City at Deh Sabz. India has also built the Friendship Dam or Salma dam which was inaugurated in June 2016.
- Significance: The project shows India’s continuing commitment to Afghanistan. The troubled peace process with the Taliban and the violence that targets journalists, officials and civil society activists across Afghanistan is a grim backdrop. India and Afghanistan are close neighbours and strategic partners. Both the countries have committed for a region free from terrorism and extremism. India also supports the “Afghan-led, Afghan-owned and Afghan-controlled” peace process to negotiate with the Taliban.
- Problems: Breach in the boundaries of the proglacial lakes can lead to large amounts of water to rush down to nearby streams and rivers. The water gains the momentum on its way by coming in contact with the sediments, rocks and other materials. This causes flooding downstream.
- Avalanche: The falling masses of snow and ice for which the speed increases as they move down the slope are called 'Avalanche'.
- New move: A committee was set up by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) on the request of some insurers. The committee has recommended to introduce the index-linked insurance policies (ILIPs).
- Index-linked insurance policies (ILIPs): The returns coming from the ILIPs will be linked to benchmark indices. ILIPs are the Insurance products linked with the benchmark indices. It includes 10-year Sovereign Bond Index, Sensex or Nifty etc. The ILIPs linked with the government bonds are less risky while those linked with the equity-based indices will go through the fluctuation in returns in accordance with the stock market performance. ILIPs are the alternative or complementary option to the current conventional guaranteed products such as annuities and savings products. It can also be used as the unit-linked insurance plans (ULIPs) with respect to the volatile markets and stressed interest rates. The ILIPs can be regarded as a life insurance policy under Section 10(10D) and taxability of the Insurance Policy Act.
- Significance: The ILIPs offer a greater transparency. Index-linked products can fit in between the traditional products with less transparency and the Unit-linked products with higher transparency. In the ILIPs the investment risks will be completely borne by the policyholders as in the cases of Unit-Linked products.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): It is an autonomous, statutory body. It regulates and promotes the insurance and re-insurance industries of India. The body was established under the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999. Its headquarters are in Hyderabad, Telangana. The headquarter moved from Delhi to Telangana in 2001. IRDAI comprises of 10-member namely the chairman, five full-time members and four part-time members who are appointed by the government of India. Presently, Dr. Subhash C. Khuntia is the chairman of the body.
- Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP): It is a product offered by insurance companies. The product provides the investors both the insurance and the investment under an integrated plan. The policy holders can customize the investment plan according to them. In India, the first ULIP was launched by the Unit Trust of India (UTI).
- Latest: In the Union Budget 2021-2022, total of Rs.913.43 crores have been dedicated to the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR). This amount to 32% increase in the revised estimate of budget 2020-21.
- Distribution:
- Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA)- Out of the Rs. 913.43 crores, Rs.593 crores have been provided under the Scheme Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA). It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, with the aim to strengthen Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Its primary focus is on its convergence with Mission Antyodaya by the capacity building of the rural local governments.
- SVAMITVA scheme – Rs.200 crores has been allocated for scheme-SVAMITVA, that seeks to provide the ‘record of rights’ to village household owners. It will also issue the property cards for the property owners through survey of village areas, and survey would be done using the drone technology by Survey of India. For the pilot phase, a Budget Outlay of Rs.79.65 crore have been allocated. In 1432 villages, the property cards have been prepared and distributed or is under distribution to about 2.30 lakh property holders.
- Continuous Operating Reference System (CORS) network: Under the SVAMITVA scheme, 210 CORS are being set up in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh. SVAMITVA Scheme aims that the CORS network reaches all across the Country by 2022. The CORs networks are used by any State agency or Department namely, the Revenue Department, Public Works Department, Gram Panchayat (GP), Agriculture, Rural Development Department, Education, Drainage & Canal, Water, Electricity, Health etc. to survey the works and implementation of schemes. This network uses the GIS based applications to survey the works. It overhauls the traditional survey system in the rural areas. The network provides accuracy up to 5 centimetre-level in real-time.
9.1 Today's best editorials to read
- We offer you 7 excellent editorials from across 10 newspapers we have scanned.
- [message]
- SECTION 3 - MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)